Queue
Enqueue messages and entities
Libraries:
Simulink /
Messages & Events
SimEvents
Alternative Configurations of Queue Block:
Entity Queue
Description
This block stores entities or messages in a queue, based on their order of arrival or priority. Each element at the head of the queue departs when the downstream block is ready to accept it.
You can specify the capacity of the queue, and the policy when the queue is full. The block supports three different message or queue sorting policies, first-in-first out (FIFO), last-in-first out (LIFO), and priority. The priority queue can be used only when the Overwrite the oldest element if queue is full check box is cleared.
Examples
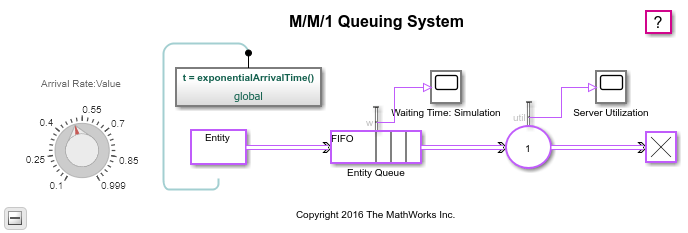
M/M/1 Queuing System
An M/M/1 queue is a queuing system that has a Poisson arrival process, an exponential service time distribution, and one server. This example models an M/M/1 queuing system with a single traffic source and infinite storage capacity.
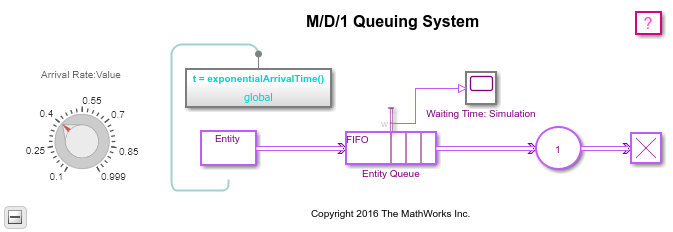
M/D/1 Queuing System
Model a single-queue single-server system that has a Poisson arrival process and a server with constant service time. The queue has an infinite storage capacity. In the notation, the M stands for Markovian; M/D/1 means that the system has a Poisson arrival process, a deterministic service time distribution, and one server.
G/G/1 Queuing System and Little's Law
Model a single-queue single-server system in which the interarrival time and the service time are uniformly distributed with fixed means of 1.1 and 1, respectively. The queue has an infinite storage capacity. In the notation, the G stands for a general distribution with a known mean and variance; G/G/1 means that the system's interarrival and service times are governed by such a general distribution, and that the system has one server. You can change the variances of the uniform distributions. You can use this model to examine Little's law.
Modeling Hybrid Systems - Tank Filling
A hybrid system with both continuous time and discrete event sections. The discrete event part models tanks, represented by entities, which are being queued and need to be filled up. Each tank has a "Capacity" attribute. The continuous time part models the process of filling up a tank, modeled by an Integrator. When a tank is filled to capacity, this event can be detected by a Hit Crossing block, which will generate a message corresponding to this event. The generated message will trigger the server to release the tank.
Model Traffic Intersections as a Queuing Network
Create a SimEvents® model to represent a vehicle traffic network and to investigate mean waiting time of vehicles when the network is in steady-state.
Ports
Input
Input entity or message that carries scalar, bus, or vector data to enter the queue.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | enumerated | bus | fixed point
Output
Output port that allows entities or messages at the head of the queue to depart when a downstream block is ready to accept them.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | enumerated | bus | fixed point
Number of entities that have departed the block.
Dependencies
To enable this port, in the Statistics tab, select the Number of entities departed, d check box.
Data Types: double
Number of entities that have not yet departed the block.
Dependencies
To enable this port, in the Statistics tab, select the Number of entities in block, n check box.
Data Types: double
Average wait time for entities in the block.
Dependencies
To enable this port, in the Statistics tab, select the Average wait, w check box.
Data Types: double
Port_l outputs the average length of the entity queue.
Dependencies
To enable this port, in the Statistics tab, select the Average queue length, l check box.
Data Types: double
Number of entities that are pulled out of this block.
Dependencies
To enable this port, in the Statistics tab, select the Number of entities extracted, ex check box.
Data Types: double
Parameters
Select this check box to choose between two queue overwriting policies.
If you select the check box, an incoming message overwrites the oldest if the queue is full.
This mode represents a simple message buffer that you can use to generate asynchronous communication between Simulink components and production code.
If you clear the check box, the block does not accept new messages if the queue is full.
In this mode, you can manipulate entity data using event actions and visualize statistics.
To customize actions when entities or messages enter, exit, or are blocked, enter MATLAB® code in the
Entry action,Exit action, orBlocked actionfield of the Event actions tab. For more information, see Events and Event Actions.For an example, see Manage Entities Using Event Actions.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
QueueOverwriting |
| Type: character vector |
Values: 'on'
| 'off' |
Default:
'on' (for Simulink) and 'off' (for SimEvents) |
Specify the capacity of the queue.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
Capacity |
| Type: character vector |
Values: '25'
| scalar |
Default:
'25' |
Choose the queue type.
FIFO— first-in-first-outLIFO— last-in-first-outPriority— store elements in order of priority, see Serve High-Priority Customers by Sorting Entities Based on Priority.Prioritycan be selected when you clear the Overwrite the oldest element if queue is full check box.Note
Priority queue does not support
fixed pointdata type.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
QueueType |
| Type: character vector |
Values:
'FIFO' | 'LIFO' |
'Priority' |
Default:
'FIFO' |
Specify the tag when accepting entities broadcast via multicast sources. The Entity Multicast block requires SimEvents license.
Dependencies
This parameter is visible when you clear the Overwrite the
oldest element if queue is full check box, and set
Entity arrival source to
Multicast.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
MulticastTag |
| Type: character vector |
Values: 'A'
| character vector |
Default:
'A' |
Specify the priority source either as a custom entity attribute that you
created, or the entitySys.priority attribute,
specifically.
For example, assume that you added two new attributes named
height and width for an entity in
the Entity Type tab of a Entity Generator block. These
attributes appear as options, in the form of character vectors, for the
Priority source parameter. The value of the
parameters determine the entity priority.
Note
If you do not replace the default text prompt, PriorityAttribute, with a priority source, then the model generates an error during compilation.
Dependencies
This parameter is visible when you clear the Overwrite the
oldest element if queue is full check box, and set
Queue type to
Priority.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
PrioritySource |
| Type: character vector |
Values:
'entity' |
'entitySys.priority' | character
vector |
Choose the direction of sorting based on priority.
Ascending— Elements with smaller priority values appear in front of the queue.Descending— Elements with greater priority values appear in front of the queue.
Dependencies
This parameter is visible when you clear the Overwrite the
oldest element if queue is full check box, and set
Queue type to
Priority.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
SortingDirection |
| Type: character vector |
Values:
'Ascending' | 'Descending'
|
Default:
'Ascending' |
Choose the source of arrival for the entities.
Input port— Input port is source of messages or entities.Multicast— Entity Multicast block is source of entities. The Entity Multicast block requires SimEvents license.
Dependencies
This parameter is visible when you clear the Overwrite the oldest element if queue is full check box.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
EntityArrivalSource |
| Type: character vector |
Values: 'Input
port' | 'Multicast'
|
Default: 'Input
port' |
Specify the behavior of the entity in certain events. Define the behavior in the Event action parameter. The Entry and the Exit actions are called just after the entity entry and just before entity exit. The Blocked action is called after an entity is blocked. For more information, see Events and Event Actions.
Note
If an event action changes an entity, related block behavior such as resorting a priority queue, and rescheduling of any events, will occur after the event action has fully finished and returned.
Note
Event actions do not support fixed point data
type.
Dependencies
Event actions are visible when you clear the Overwrite the oldest element if queue is full check box.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
EntryAction, ExitAction,
BlockedAction |
| Type: character vector |
| Values: MATLAB code |
Default:
'' |
Number of entities that have departed the block.
Dependencies
Number of entities departed, d is visible when you clear the Overwrite the oldest element if queue is full check box.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
NumberEntitiesDeparted |
| Type: character vector |
Values: 'on'
| 'off' |
Default:
'off' |
Number of entities present in the block, but which are yet to depart.
Dependencies
Number of entities in block, n is visible when you clear the Overwrite the oldest element if queue is full check box.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
NumberEntitiesInBlock |
| Type: character vector |
Values: 'on'
| 'off' |
Default:
'off' |
Sum of the wait times for entities departing the block divided by their total number. Wait time is the duration between the Entity Queue block entry and exit of an entity. For more information, see Interpret SimEvents Models Using Statistical Analysis.
Dependencies
Average wait, w is visible when you clear the Overwrite the oldest element if queue is full check box.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
AverageWait |
| Type: character vector |
Values: 'on'
| 'off' |
Default:
'off' |
Accumulated time-weighted average queue size. The block computes this value by:
Multiplying the size of the queue by its duration to calculate time-weighted queue size
Summing up all time-weighted queue sizes and averaging them over total time
For more information, see Interpret SimEvents Models Using Statistical Analysis.
Dependencies
Average queue length, l is visible when you clear the Overwrite the oldest element if queue is full check box.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
AverageQueueLength |
| Type: character vector |
Values: 'on'
| 'off' |
Default:
'off' |
Outputs the number of extracted entities which are pulled out from this block by the Entity Find block. The Entity Find block requires a SimEvents license. If the extracted entity is the first entity in the queue, the next entity is set as the pending entity to leave the block. If an entity attribute defines the priority in a priority queue and it is modified by the Entity Find block, the queue is sorted again. When an entity is extracted, Number of entities departed, d, Number of entities in block, n, Average wait, w, and Average queue length, l statistics are updated accordingly. For more information about finding and extracting entities, see Find and Extract Entities in SimEvents Models.
Dependencies
Number of entities extracted, ex is visible when you clear the Overwrite the oldest element if queue is full check box.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
NumEntitiesExtracted |
| Type: character vector |
Values: 'on'
| 'off' |
Default:
'off' |
Block Characteristics
Data Types |
|
Direct Feedthrough |
|
Multidimensional Signals |
|
Variable-Size Signals |
|
Zero-Crossing Detection |
|
Alternative Configurations
The Entity Queue block clears the Overwrite the oldest element if queue is full parameter, sets the Capacity parameter to 25, and sets the Queue type parameter to FIFO.
Libraries:
Simulink /
Messages & Events
SimEvents
Extended Capabilities
Code generation is not supported for event actions and statistics.
When you generate code for a model that contains a message queue and has multitasking enabled, enable concurrent tasking behavior if that model will be deployed to a multitasking environment. Otherwise, the generated code has the potential for data corruption. You enable concurrent tasking behavior by selecting Allow tasks to execute concurrently on target.
Version History
Introduced in R2016a
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleccione un país/idioma
Seleccione un país/idioma para obtener contenido traducido, si está disponible, y ver eventos y ofertas de productos y servicios locales. Según su ubicación geográfica, recomendamos que seleccione: .
También puede seleccionar uno de estos países/idiomas:
Cómo obtener el mejor rendimiento
Seleccione China (en idioma chino o inglés) para obtener el mejor rendimiento. Los sitios web de otros países no están optimizados para ser accedidos desde su ubicación geográfica.
América
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)