Create C Package Using C Shared Library Compiler App
Supported platforms: Windows®, Linux®, Mac
This example shows how to use the C Shared Library Compiler app to package a MATLAB® function into a C shared library. You can call the package in a provided C application that displays the Sierpinski's Triangle fractal.
Before R2025a: Create a C shared library using the Library Compiler as shown in Create a C Shared Library with MATLAB Code (R2024b).
Prerequisites
Verify that you have a C compiler that is compatible with MATLAB Compiler SDK™. For a list of platform-specific supported C compilers, see Supported and Compatible Compilers on the MathWorks® website.
End users must have an installation of MATLAB Runtime to run the application. For details, see Download and Install MATLAB Runtime.
For testing purposes, you can use an installation of MATLAB instead of MATLAB Runtime.
Write Deployable MATLAB Code
In MATLAB, examine the MATLAB code that you want to package. This example uses these files in
:
\extern\examples\compilersdk\c_cpp\trianglematlabroot
| MATLAB Function |
sierpinski.m
|
| C Application Code |
triangle.c
|
The function sierpinski.m uses a simple iterative algorithm to
generate the fractal known as Sierpinski's Triangle. The main program optionally can take a
single numeric argument that specifies the number of points used to generate the fractal.
For example, triangle 8000 generates a diagram with 8,000
points.
At the MATLAB command prompt, copy the contents of the triangle folder
that ships with MATLAB to a new folder named TriangleProject.
copyfile(fullfile(matlabroot,"extern","examples", ... "compilersdk","c_cpp","triangle"),"TriangleProject")
Examine the function
sierpinski.m.
function [x, y] = sierpinski(iterations, draw) % SIERPINSKI Calculate (optionally draw) the points in Sierpinski's triangle % Copyright 2004-2018 The MathWorks, Inc. % Three points defining a nice wide triangle points = [0.5 0.9 ; 0.1 0.1 ; 0.9 0.1]; % Select an initial point current = rand(1, 2); % Create a figure window if (draw == true) f = figure; hold on; end % Pre-allocate space for the results, to improve performance x = zeros(1,iterations); y = zeros(1,iterations); % Iterate for i = 1:iterations % Select point at random index = floor(rand * 3) + 1; % Calculate midpoint between current point and random point current(1) = (current(1) + points(index, 1)) / 2; current(2) = (current(2) + points(index, 2)) / 2; % Plot that point if draw, line(current(1),current(2),'Marker','.','MarkerSize',1);, end x(i) = current(1); y(i) = current(2); end if (draw) drawnow; end
Create Project and Compiler Task
Create a compiler task for your C shared library using the C Shared Library Compiler. Compiler tasks allow you to compile files in a project for a specific deployment target.
To open the app, on the Apps tab, expand the Apps gallery. In the Application Deployment section, click C Shared Library Compiler.
You can also open the app using the cSharedLibraryCompiler function
at the MATLAB Command Window.
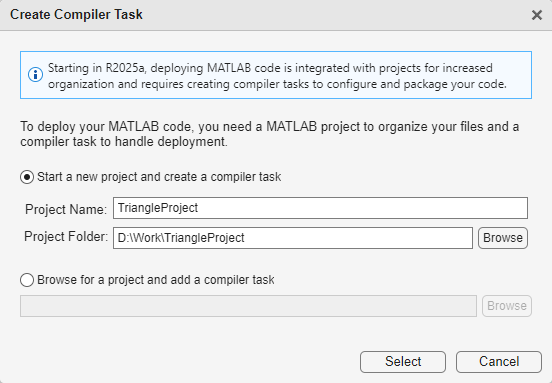
After you open the app, the Create Compiler Task dialog box prompts you to add a
compiler task to a new or an existing MATLAB project. For this example, select Start a new project and create a
compiler task and create a new project named
TriangleProject in your working folder. For more information on
creating and using MATLAB projects, see Create Projects.
A new compiler task named CSharedLib1 opens in the Editor. You can
compile code for other deployment targets by opening the Compiler Task Manager
or going to the Manage Tasks tab and creating a new compiler
task.
Specify Build Options
You can specify options for the C shared library and its installer before packaging to customize the building and packaging process. For instance, you can obfuscate the MATLAB code or specify the method of including MATLAB Runtime in the generated installer.
Add the MATLAB functions to the C shared library. All files must be located in the project
root folder to be added to the project. For this example, in the Exported
Functions section of the compiler task, click Add File
and select sierpinski.m. In the Project panel, the file now has the
labels Design and Exported Function File.

In the Package Info section, replace the string My C
Package with the name for your C shared library,
libtriangle.
View Code and Package C Shared Library
To view code that contains instructions on building and packaging your component, click
the arrow next to Export Build Script and select Show
Code. On the right, a window displays a deployment script with the compiler.build.cSharedLibrary and compiler.package.installer functions that corresponds to your build options.
You can convert this code to a MATLAB script file by clicking the Export Build Script button.
Running the generated build script is equivalent to clicking the Build and
Package button.
![]()
To create the C shared library and an installer, click Build and Package. To create only the C shared library, click the arrow next to Build and Package and select Build.
The compiler generates files in the
<compiler_task_name>/output
If you created an installer, the package subfolder contains the
installer for your shared library files along with MATLAB Runtime.
Caution
The generated installer does not include a C application executable. You must
compile and link your C application using mbuild after packaging.
Then, manually distribute the application file along with MATLAB Runtime or include the executable in an installer using the
AdditionalFiles option of compiler.package.installer. For more information, see Distribute MATLAB Compiler SDK Files to Application Developers.
Compile and Run C Application
After creating the C shared library, write source code for a C application that calls the MATLAB functions in the package.
The C application included with this example is named
triangle.c.
Copy and paste the generated shared library libtriangle.lib into the
project folder that contains your C application.
Note
The .lib extension is used on Windows. On macOS, the file extension is .dylib, and on Linux it is .so.
Compile and link the application using mbuild at the MATLAB prompt or your system command prompt. This command uses your C compiler to
compile and link the code with the MATLAB
Compiler SDK generated C shared
library.
mbuild triangle.c libtriangle.lib
Run the application from the system command prompt. To test your application in
MATLAB before deployment, run the executable using the bang (!)
operator.
triangle.exe 8000The application displays the Sierpinski's Triangle figure with 8,000 points.

To run the C application outside of MATLAB, you must install MATLAB Runtime. For details, see Download and Install MATLAB Runtime. If you create an installer using Build and Package, the installer contains a version of MATLAB Runtime that matches the version of MATLAB used to compile the C shared library.
To deploy the C application, distribute the shared library and the executable
.exe file to the end user.
See Also
C Shared
Library Compiler | compiler.build.cSharedLibrary | compiler.package.installer | mbuild
