Linux Task
Spawn task function as separate Linux thread
Add-On Required: This feature requires the Embedded Coder Support Package for AMD SoC Devices add-on.
Libraries:
Embedded Coder Support Package for AMD SoC Devices
Description
Use this block to create a task function that spawns as a separate Linux® thread. The task function runs the code of the downstream Function-Call Subsystem block.
Examples
Get Started with Embedded Coder Support Package for AMD SoC Devices
Generate code from a Simulink® model and run the executable on an AMD Zynq® board.
Ports
Output
A function-call control signal that triggers a Function-Call Subsystem block.
Parameters
To edit block parameters interactively, use the Property Inspector. From the Simulink® Toolstrip, on the Simulation tab, in the Prepare gallery, select Property Inspector.
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use
the set_param function.
To get the block parameter value
programmatically, use the get_param function.
Assign a name to this task. You can enter up to 32 letters and numbers. Do not use
standard C reserved characters, such as the / and
: characters.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
taskName
|
Select the scheduling policy that applies to this thread. You can choose from these options:
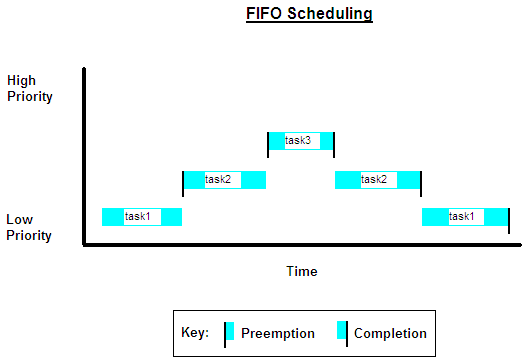
SCHED_FIFO— This option enables a first-in, first-out (FIFO) scheduling algorithm that executes real-time processes without time slicing. With FIFO scheduling, a higher-priority process preempts a lower-priority process. The lower-priority process remains at the top of the list for its priority and resumes execution when the scheduler blocks all higher-priority processes.For example, in the FIFO scheduling image, task2 preempts task1. Then, task3 preempts task2. When task3 completes, task2 resumes. When task2 completes, task1 resumes.
Selecting
SCHED_FIFOdisplays the Thread priority parameter, which you can set to a value from 1 to 99.SCHED_OTHER— This option enables the default Linux time-sharing scheduling algorithm. You can use this scheduling for all processes except those requiring special static priority real-time mechanisms. With this algorithm, the scheduler chooses processes based on their dynamic priority within the static priority 0 list. Each time the process is ready to run and the scheduler denies it, the operating system increases the dynamic priority of that process. Such prioritization helps the scheduler serve theSCHED_OTHERprocesses.Selecting
SCHED_OTHERhides the Thread priority parameter and sets the thread priority to 0.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
taskPolicy
|
Specify the priority of the Linux thread. A value of 1 indicates a low priority, and a value of 99 indicates a high priority. Higher-priority tasks can preempt lower-priority tasks.
To enable this parameter, set Thread scheduling policy to
SCHED_FIFO.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
taskPriority
|
Version History
Introduced in R2013a
See Also
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleccione un país/idioma
Seleccione un país/idioma para obtener contenido traducido, si está disponible, y ver eventos y ofertas de productos y servicios locales. Según su ubicación geográfica, recomendamos que seleccione: .
También puede seleccionar uno de estos países/idiomas:
Cómo obtener el mejor rendimiento
Seleccione China (en idioma chino o inglés) para obtener el mejor rendimiento. Los sitios web de otros países no están optimizados para ser accedidos desde su ubicación geográfica.
América
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)
