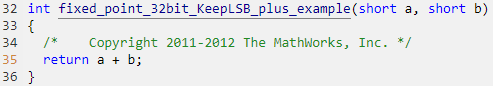
removefimath
Remove fimath from fi object
Syntax
Description
y = removefimath(x)fi object y with x’s
numerictype and value and with no fimath object
attached.
You can use this function as y = removefimath(y), which gives you
localized control over the fimath settings. This function also is useful
for preventing errors about embedded.fimath of both
operands needing to be equal.
Examples
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2012b