chromosomeplot
Plot chromosome ideogram with G-banding pattern
Description
chromosomeplot( plots the ideogram of
all chromosomes, using information from cytogenetic G-banding data
CytoData)CytoData.
chromosomeplot(___,
specifies additional options using one or more name-value arguments.Name=Value)
Examples
Read the cytogenetic banding information for Homo sapiens into a structure.
hs_cytobands = cytobandread('hs_cytoBand.txt')hs_cytobands = struct with fields:
ChromLabels: {862×1 cell}
BandStartBPs: [862×1 int32]
BandEndBPs: [862×1 int32]
BandLabels: {862×1 cell}
GieStains: {862×1 cell}
Plot the entire chromosome ideogram.
chromosomeplot(hs_cytobands);
title('Human Karyogram')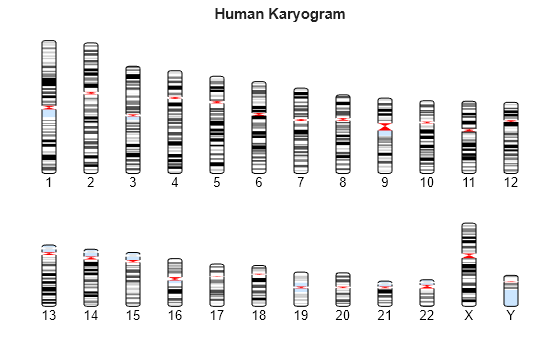
You can display the ideogram of a specific chromosome by right-clicking it in the plot, then selecting Display in New Figure > Vertical or Horizontal.
You can also programmatically display the ideogram of a specific chromosome, set the orientation, and the units used in the data tip to kilo base pairs.
chromosomeplot(hs_cytobands, 15, 'Orientation', 2, 'Unit', 2);
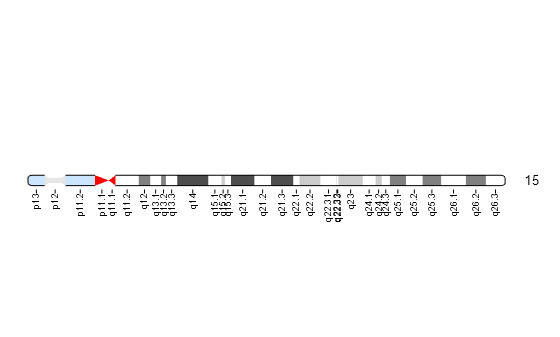
Hover over the chromosome to view a data tip. To get more information about a specific band, select the Data Cursor button on the toolbar and click the band in the plot. Use the context menu (right-click) to see more options such as deleting or creating a data tip.
Load the array-based CGH (aCGH) data from the Coriell cell line study (Snijders, A. et al., 2001).
load coriell_baccghUse the cghcbs function to analyze chromosome 10 of sample 3 (GM05296) of the aCGH data and return copy number variance (CNV) data in a structure, S. Plot the segment means over the original data for only chromosome 10 of sample 3.
S = cghcbs(coriell_data,'sampleindex',3,'chromosome',10,... 'showplot',10);
Analyzing: GM05296. Current chromosome 10

Use the chromosomeplot function with the 'addtoplot' option to add the ideogram of chromosome 10 for Homo sapiens to the plot. Because the plot of the CNV data from the Coriell cell line study is in kb units, use the 'Unit' property to convert the ideogram data to kb units.
set(gcf,'color','w'); % Set the background of the figure to white. chromosomeplot('hs_cytoBand.txt', 10, 'addtoplot', gca,... 'Unit', 2);

Input Arguments
Cytogenetic G-banding data in bp units, specified as a structure, or character vector or string scalar representing the name of a file.
If CytoData is a structure, it must contain the cytogenetic
G-banding data with the following fields:
ChromLabelsBandStartBPsBandEndBPsBandLabelsGieStains
The cytobandread function creates such a
structure.
If CytoData is a file name, the file must contain cytogenetic
G-banding data. For example, the file can be an NCBI ideogram text file or a UCSC Genome
Browser cytoband text file.
The G bands distinguish different areas of the chromosome. For example, for the Homo sapiens ideogram, possible G bands are:
gneg— whitegpos25— light graygpos50— medium graygpos75— dark graygpos100— blackacen— red (centromere)stalk— indented region (region with repeats)gvar— light blue
Darker bands are AT-rich, while lighter bands are GC-rich.
Data Types: char | string | struct
Chromosome to plot, specified as a nonnegative scalar, "X", or
"Y".
By default, the function plots ideograms for all chromosomes.
Data Types: double | char | string
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: chromosomeplot(hs_cytobands,15,Orientation=2) plots
chromosome 15 in the horizontal orientation.
Orientation of a specified chromosome to plot, specified as
"Vertical" or 1 or "Horizontal" or 2.
You must specify a single chromosome for this name-value argument to work.
When plotting the ideogram of all chromosomes, the orientation is always vertical.
Data Types: double | char | string
Flag to display band labels of a specified chromosome, specified as a numeric or
logical true (1) or false (0).
You must specify a single chromosome for this name-value argument to work.
Data Types: double | logical
Axes handle of a figure to which to add a single chromosome ideogram, specified as an axes handle.
If you use this property to add the ideogram to a plot of genomic data that is in
units other than bp, use the Unit argument to convert the
ideogram data to the appropriate units.
Tip
Before printing a figure containing an added chromosome ideogram, change the
background to white by issuing the following command:
set(gcf,'color','w').
Unit for the starting and ending genomic positions, specified as 1 (bp), 2 (kb), or 3 (mb).
This unit is used in the data tip displayed when you hover the cursor over
chromosomes in the ideogram. This unit can also be used when using the
AddToPlot argument to add the ideogram to a plot that is in
units other than bp.
Data Types: double
Option to control the display of copy number variance data aligned to the chromosome ideogram, specified as a scalar structure.
Gains are shown in green to the right or above the ideogram, while losses are shown in red to the left or below the ideogram.
The structure has the following fields. Each field must contain the same number of elements.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Chromosome | Either of the following:
|
CNVType | Numeric vector containing the type of each CNV, either
|
Start | Numeric vector containing the starting genomic position of each CNV. Units must be in base pairs. |
End | Numeric vector containing the ending genomic position of each CNV. Units must be in base pairs. |
Data Types: struct
Version History
Introduced in R2007b
See Also
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleccione un país/idioma
Seleccione un país/idioma para obtener contenido traducido, si está disponible, y ver eventos y ofertas de productos y servicios locales. Según su ubicación geográfica, recomendamos que seleccione: .
También puede seleccionar uno de estos países/idiomas:
Cómo obtener el mejor rendimiento
Seleccione China (en idioma chino o inglés) para obtener el mejor rendimiento. Los sitios web de otros países no están optimizados para ser accedidos desde su ubicación geográfica.
América
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)