Bluetooth BR/EDR Waveform Reception Using SDR
This example shows how to capture and decode Bluetooth® basic rate/enhanced data rate (BR/EDR) waveform by using Bluetooth® Toolbox. You can either capture the Bluetooth BR/EDR waveform by using the ADALM-PLUTO radio or load in-phase and quadrature phase (IQ) samples corresponding to the Bluetooth BR/EDR waveform from a baseband file (*.bb). To generate and transmit the Bluetooth BR/EDR waveform, see Bluetooth LE Waveform Generation and Transmission Using SDR and configure your test environment with:
Two SDR platforms connected to the same host computer, and run two MATLAB® sessions on the single host computer.
Two SDR platforms connected to two host computers, and run one MATLAB session on each host computer.
To configure your host computer to work with the Support Package for ADALM-PLUTO Radio, see Guided Host-Radio Hardware Setup.
Required Hardware
To capture signals in real time, you need ADALM-PLUTO radio and the corresponding support package add-on.
For a full list of communications toolboxes supported by SDR platforms, see the Supported Hardware section of the SDR discovery page.
Bluetooth BR/EDR Radio Specifications
Bluetooth is a short-range Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN) technology, operating in the globally unlicensed industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) band in the frequency range of 2.4 GHz to 2.485 GHz. In Bluetooth technology, data is divided into packets and each packet is transmitted on one of the 79 designated Bluetooth channels. Each channel has a bandwidth of 1 MHz. As there are different types of wireless networks operating in the same unlicensed frequency band, it is possible for two different networks to interfere with each other. To mitigate the interference, Bluetooth implements the frequency-hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) scheme to switch a carrier between multiple frequency channels by using a pseudorandom sequence known to both transmitter and receiver.
The Bluetooth standard specifies these physical layer (PHY) modes.
Basic rate (BR) — Mandatory mode, uses Gaussian frequency shift keying (GFSK) modulation with a data rate of 1 Mbps
Enhanced data rate (EDR) — Optional mode, uses phase shift keying (PSK) modulation with these two variants.
EDR2M: Uses /4-differential quadrature phase shift keying (DQPSK) with a data rate of 2 Mbps.
EDR3M: Uses 8-differential phase shift keying (DPSK) with a data rate of 3 Mbps.
Bluetooth BR/EDR Packet Formats
The air interface packet formats for PHY modes include these fields:
Access Code — Each packet starts with an access code. If a packet header follows, the access code is 72 bits long. Otherwise, the length of the access code is 68 bits and referred to as a shortened access code. The access code consists of these fields:
Preamble: The preamble is a fixed zero-one pattern of four symbols.
Sync Word: The sync word is a 64-bit code word derived from the 24-bit lower address part (LAP) of the Bluetooth device address.
Trailer: The trailer is a fixed zero-one pattern of four symbols.
Access Code Format

Packet Header — The header includes link control information and consists of these fields:
LT_ADDR: 3-bit logical transport address
TYPE: 4-bit type code, which specifies the packet type used for transmission. The value of this field can be ID, NULL, POLL, FHS, HV1, HV2, HV3, DV, EV3, EV4, EV5, 2-EV3, 2-EV5, 3-EV3, 3-EV5, DM1, DH1, DM3, DH3, DM5, DH5, AUX1, 2-DH1, 2-DH3, 2-DH5, 3-DH1, 3-DH3 and 3-DH5. This field determines the number of slots the current packet occupies.
FLOW: 1-bit flow control over the asynchronous connection-oriented logical (ACL) transport
ARQN: 1-bit acknowledgment indication
SEQN: 1-bit sequence number
HEC: 8-bit header error check
Header Format

Payload — Payload includes an optional payload header, a payload body, and an optional CRC. This figure shows the format of payload.
Payload Format

Guard — For EDR packets, guard time allows the Bluetooth BR/EDR radio to prepare for the change in modulation from GFSK to DPSK. The guard time must be between 4.75 to 5.25 microseconds.
Sync — For EDR packets, the synchronization sequence contains one reference symbol and ten DPSK symbols.
Trailer — For EDR packets, the trailer bits must be all zero pattern of two symbols, {00,00} for /4-DQPSK and {000,000} for 8DPSK.
This figure shows the packet format for BR mode.
Basic Rate Packet Format

This figure shows the packet format for EDR mode.
Enhanced Data Rate Packet Format

Receiver and SDR Configuration
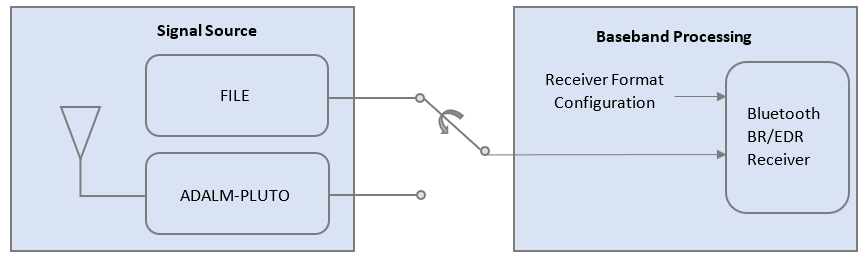
This figure shows the receiver procedure to decode Bluetooth BR/EDR waveform either captured by using ADALM-PLUTO or by reading IQ samples from a baseband file.
Bluetooth BR/EDR Receiver
Configure the Bluetooth BR/EDR parameters by using the bluetoothPhyConfig configuration object.
cfg = bluetoothPhyConfig;
Specify the PHY transmission mode as "BR", "EDR2M" or "EDR3M".
cfg.Mode =  "BR";
"BR";Initialize the whiten initialization.
cfg.WhitenInitialization = [0;0;0;0;0;1;1];
Specify the signal source as "File" or "ADALM-PLUTO".
File — Use the
comm.BasebandFileReaderSystem object™ to read a file that contains a previously captured over-the-air signal.ADALM-PLUTO — Use the
sdrrxSystem object™ to receive a live signal from the SDR hardware.
If you assign ADALM-PLUTO as the signal source, the example searches your computer for the ADALM-PLUTO radio at radio address 'usb:0' and uses it as the signal source.
signalSource =  "File";
"File";Specify the baseband symbol rate.
bbSymbolRate = 1e6; if signalSource == "File"
Specify the corresponding baseband file.
switch cfg.Mode case "BR" bbFileName = "bluetoothCapturesBR.bb"; case "EDR2M" bbFileName = "bluetoothCapturesEDR2M.bb"; case "EDR3M" bbFileName = "bluetoothCapturesEDR3M.bb"; end sigSrc = comm.BasebandFileReader(bbFileName); sigSrcInfo = info(sigSrc); bbSampleRate = sigSrc.SampleRate; sigSrc.SamplesPerFrame = sigSrcInfo.NumSamplesInData; cfg.SamplesPerSymbol = bbSampleRate/bbSymbolRate; else
Check if the ADALM-PLUTO hardware support package (HSP) add-on exists.
if isempty(which("plutoradio.internal.getRootDir")) link = sprintf('<a href="https://www.mathworks.com/hardware-support/pluto.html">ADALM-PLUTO Radio Support From Communications Toolbox</a>'); error("Unable to find Communications Toolbox Support Package for ADALM-PLUTO Radio. To install the support package, visit %s",link); end
Discover the ADALM-PLUTO radio(s) connected to your computer.
connectedRadios = findPlutoRadio;
radioID = connectedRadios(1).RadioID;Specify the receiver center frequency in Hz within 2.402 GHz to 2.480 GHz.
rxCenterFrequency =  2445000000;
2445000000;Specify the base-band sample rate.
bbSampleRate = bbSymbolRate * cfg.SamplesPerSymbol;
Create receiver System object™ for radio hardware.
sigSrc = sdrrx("Pluto", ... RadioID=radioID, ... CenterFrequency=rxCenterFrequency, ... BasebandSampleRate=bbSampleRate, ... SamplesPerFrame=1e7, ... GainSource="Manual", ... Gain=25, ... OutputDataType="double"); end
Set the configuration to display the frequency spectrum of the PHY waveform.
spectrumScope = spectrumAnalyzer(Method="welch", ... SampleRate=bbSampleRate,... SpectrumType="Power density", ... YLimits=[-130 -30], ... Title="Received Baseband Bluetooth Signal Spectrum", ... YLabel="Power spectral density");
Capture Bluetooth BR/EDR Waveforms
Capture transmitted waveform as a burst.
dataCaptures = sigSrc();
Visualize the spectrum of the received Bluetooth waveform by using a spectrum analyzer.
spectrumScope(dataCaptures)

Receiver Processing
This figure shows the workflow of receiver.
Bluetooth Practical Receiver

To decode the packet header, payload header information, and raw message bits from the received baseband samples, the Bluetooth BR/EDR receiver performs these functions:
Remove DC offset
Detect the signal bursts
Perform matched filtering
Estimate and correct the timing offset
Estimate and correct the carrier frequency offset
Demodulate BR/EDR waveform
Perform forward error correction (FEC) decoding
Perform data de-whitening
Perform header error check (HEC) and cyclic redundancy check (CRC)
Outputs decoded bits and decoded packet statistics based on decoded lower address part (LAP), HEC and CRC
Extract the message information by using the helperBluetoothPracticalReceiver helper function.
[decBits,decodedInfo,pktStatus] = helperBluetoothPracticalReceiver(dataCaptures,cfg);
Compute the number of packets.
pktCount = length(pktStatus);
disp("Number of Bluetooth packets detected: "+num2str(pktCount))Number of Bluetooth packets detected: 2
Enable the displayFlag flag to print the decoded packet statistics.
displayFlag =true; if displayFlag && (pktCount~=0) decodedInfoPrint = decodedInfo; for ii = 1:pktCount if(pktStatus(ii)) decodedInfoPrint(ii).PacketStatus = "Success"; else decodedInfoPrint(ii).PacketStatus = "Fail"; end end packetInfo = struct2table(decodedInfoPrint,"AsArray",1); fprintf("Decoded Bluetooth packet(s) information: \n \n") disp(packetInfo); end
Decoded Bluetooth packet(s) information:
LAP PacketType LogicalTransportAddress HeaderControlBits PayloadLength LLID FlowIndicator PacketStatus
_____________ __________ _______________________ _________________ _____________ ____________ _____________ ____________
{24×1 double} {'FHS'} {3×1 double} {3×1 double} 18 {2×1 double} 0 "Success"
{24×1 double} {'FHS'} {3×1 double} {3×1 double} 18 {2×1 double} 0 "Success"
Compute the packet error rate (PER) performance metrics based on the decoded packet information.
if(pktCount) pktErrCount = sum(~pktStatus); pktErrRate = pktErrCount/pktCount; disp("Simulated Mode: "+cfg.Mode+", " + ... "Packet error rate: "+num2str(pktErrRate)) end
Simulated Mode: BR, Packet error rate: 0
Release the signal source.
release(sigSrc)
Further Exploration
You can explore and run the Bluetooth BR/EDR Waveform Generation and Transmission Using SDR example to generate and transmit a standard-compliant Bluetooth BR/EDR waveform by using the SDR. Then, use this example to demodulate and decode the BR/EDR waveform by changing the PHY transmission mode.
Troubleshooting
General tips for troubleshooting SDR hardware and the Communications Toolbox Support Package for ADALM-PLUTO Radio can be found in Common Problems and Fixes.
Appendix
This example uses this helper function:
helperBluetoothPracticalReceiver— Practical receiver for Bluetooth PHY
Selected Bibliography
Bluetooth Technology Website. “Bluetooth Technology Website | The Official Website of Bluetooth Technology.” Accessed September 20, 2024. https://www.bluetooth.com/
Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG). "Bluetooth Core Specification". Version 5.3. https://www.bluetooth.com/