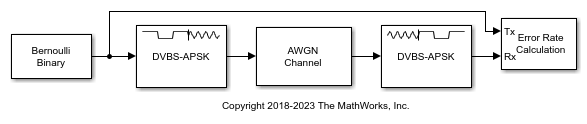
DVBS-APSK Demodulator Baseband
DVB-S2/S2X/SH standard-specific amplitude phase shift keying (APSK) demodulation
Libraries:
Communications Toolbox /
Modulation /
Digital Baseband Modulation /
APM
Communications Toolbox /
Modulation /
Digital Baseband Modulation /
Standard-Compliant
Description
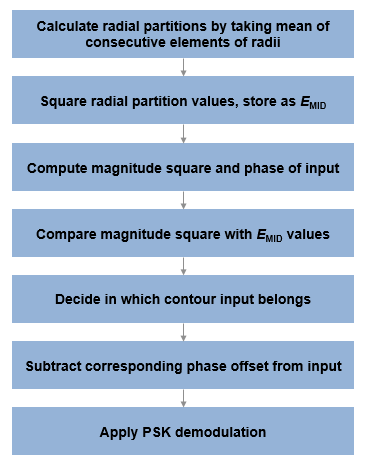
The DVBS-APSK Demodulator Baseband block demodulates the input signal using Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB-S2/S2X/SH) standard-specific amplitude phase shift keying (APSK) demodulation. For a description of DVB-compliant APSK demodulation, see DVB Compliant APSK Hard Demodulation and DVB Compliant APSK Soft Demodulation.
This icon shows the block with all ports enabled: ![]()
Examples
Ports
Input
Output
Parameters
Block Characteristics
Data Types |
|
Multidimensional Signals |
|
Variable-Size Signals |
|
More About
Tips
For faster execution of the DVBS-APSK Demodulator Baseband block, set the Simulate using parameter to:
Code generationwhen using hard decision demodulation.Interpreted executionwhen using soft decision demodulation.
References
[1] ETSI Standard EN 302 307 V1.4.1: Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB); Second generation framing structure, channel coding and modulation systems for Broadcasting, Interactive Services, News Gathering and other broadband satellite applications (DVB-S2), European Telecommunications Standards Institute, Valbonne, France, 2005-03.
[2] ETSI Standard EN 302 307-2 V1.1.1: Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB); Second generation framing structure, channel coding and modulation systems for Broadcasting, Interactive Services, News Gathering and other broadband satellite applications (DVB-S2X), European Telecommunications Standards Institute, Valbonne, France, 2015-02.
[3] ETSI Standard EN 302 583 V1.1.1: Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB); Framing structure, channel coding and modulation for Satellite Services to Handheld devices (SH), European Telecommunications Standards Institute, Valbonne, France, 2008-03.
[4] Sebesta, J. “Efficient Method for APSK Demodulation.” Selected Topics on Applied Mathematics, Circuits, Systems, and Signals (P. Pardalos, N. Mastorakis, V. Mladenov, and Z. Bojkovic, eds.). Vouliagmeni, Athens, Greece: WSEAS Press, 2009.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2018b