Downsample
Resample input at lower rate by deleting samples
Libraries:
DSP System Toolbox /
Signal Operations
DSP System Toolbox HDL Support /
Signal Operations
Description
The Downsample block decreases the sampling rate of the input by deleting samples. When the block performs frame-based processing, it resamples the data in each column of the Pi-by-Q input matrix independently. When the block performs sample-based processing, it treats each element of the input as a separate channel and resamples each channel of the input array across time. The resample rate is M times lower than the input sample rate, where M is the value of the downsample factor. The Downsample block resamples the input by discarding M–1 consecutive samples following each sample that is output.
This block supports triggered subsystems when you set the Rate
options parameter to Enforce single-rate
processing.
Examples
In this example, the Downsample block decreases the sample rate by decreasing the frame size.
Open the ex_downsample_singlerate.slx model. The Downsample block resamples a single-channel input with a frame size of 64. In the dialog box of the Downsample block, the Downsample factor source parameter is set to Input port. This sets the Input processing and the Rate options parameters automatically to Columns as Channels (frame based) and Enforce single-rate processing, respectively. Specify a downsample factor of 4 from the input port.
Run the model. The block operates in the single-rate processing mode and downsamples the input by a factor of 4. The output of the block has a frame size of 64. As the block operates in the single-rate processing mode, the input and output signals of the Downsample block have the same frame rate. You can confirm this from the Timing Legend. To open the legend, click the Debug tab on the model toolstrip and click Information Overlays > Timing Legend.

In this example, the Downsample block decreases the sample rate by decreasing the frame rate.
Open the ex_downsample_multirate.slx model. The input to the Downsample block is a single-channel signal with a frame period of one second. In the block dialog box, set the Downsample factor, M to 4 and Rate options to Allow multirate processing.
Run the model. The block operates in the multirate frame-based processing mode. With a downsample factor of 4, the output of the block has a frame period of 4 seconds. You can confirm this from the Timing Legend. To open the legend, click the Debug tab on the model toolstrip and click Information Overlays > Timing Legend. As the block operates in the multirate processing mode, the input and output signals of the Downsample block have the same frame size.

Downsample a signal by a factor of 2 using the Downsample block.
Open the System and Run the Model

The Signal From Workspace block generates a two-channel signal with a frame size of 4. The timing legend shows the sample time of the signal before and after the downsampling operation. To see the legend, click the Debug tab > Information Overlays > Timing Legend.
Run the model. The sample time of the signal before the downsampling operation is half the sample time of the signal after the operation.
One-Frame Latency
The Input processing parameter in the Downsample block is set to Columns as channels (frame based) and the input frame size (number of rows in the input) Mi is greater than 1. Hence, the latency of the signal is one frame. The Initial conditions parameter is set to [11 -11;12 -12;13 -13;14 -14]. In all cases of one-frame latency, the Mi rows of the initial condition matrix appear in sequence as the first four output rows. Input sample D+1 (that is, row D+1 of the input matrix) appears in the output as sample Mi+1, followed by input sample D+1+K, input sample D+1+2K, and so on.
Mi - Number of input rows. In this example, Mi equals 4.
D - Sample offset parameter. In this example, D equals 1.
K - Downsample factor. In this example, K equals 2.
The Initial conditions value can be an Mi-by- N matrix containing one value for each channel, or a scalar to be repeated across all elements of the Mi-by- N matrix.
Here is the downsampled output signal written to the dsp_examples_yout variable in the base workspace.
dsp_examples_yout =
11 -11
12 -12
13 -13
14 -14
2 -2
4 -4
6 -6
8 -8
10 -10
12 -12
14 -14
16 -16
18 -18
20 -20
22 -22
24 -24
26 -26
28 -28
30 -30
32 -32
34 -34
36 -36
38 -38
40 -40
42 -42
44 -44
46 -46
48 -48
50 -50
52 -52
54 -54
56 -56
58 -58
60 -60
62 -62
64 -64
66 -66
68 -68
70 -70
72 -72
74 -74
76 -76
78 -78
80 -80
82 -82
84 -84
86 -86
88 -88
90 -90
92 -92
94 -94
96 -96
98 -98
100 -100
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0
Extended Examples
Acoustic Noise Cancellation (LMS)
Use the least mean square (LMS) algorithm to subtract noise from an input signal. The example uses a preconfigured Simulink® model. The LMS Filter block in the dspanc model models an adaptive filter that uses the reference signal at its Input port and the desired signal at the Desired port to automatically match the filter response. The LMS Filter block subtracts the filtered noise from the original signal. As the filter converges, the resultant error signal contains only the original signal.
Ports
Input
Input data for which you want to decrease the sample rate, specified as a column vector or a matrix.
When you set the Input processing parameter to
Elements as channels (sample based), the
input can be an N-D array.
The block supports variable-size input signals when you set
Input processing to Columns as
channels (frame based) and Rate
options to Enforce single-rate
processing, so the frame length (number of rows) and
the number of channels (columns) can change during simulation. When the
block accepts variable-size input signals, they can be of arbitrary
frame length, that is, the input frame length does not have to be a
multiple of the downsampling factor. When you specify fixed-size
signals, the frame length can be arbitrary under certain conditions. For
more details, see Frame-Based Processing and
Sample-Based Processing.
This port is unnamed until you
set Downsample factor source to Input
port. (since R2023a)
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point
Complex Number Support: Yes
Since R2023a
Specify the downsample factor M as a positive integer.
Dependency
To enable this port, set the Downsample factor
source parameter to Input
port.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32
Output
Downsampled output with a sampling rate that is 1/M times the input sampling rate, returned as a column vector or a matrix.
When you set Rate options to:
Enforce single-rate processing–– The block maintains the input sample rate and downsamples the signal by decreasing the output frame size by a factor of M.The output has an upper bound size of
ceil(P/M)-by-Q for an input of size P-by-Q.Allow multirate processing–– The block downsamples the signal such that the output sample rate is M times slower than the input sample rate.The output frame size is the same as the input frame size.
For more details, see Frame-Based Processing and Sample-Based Processing.
The output is a variable-size signal when any of these conditions are met:
The input is a variable-size signal.
The input is a fixed-size signal and the Allow arbitrary frame length for fixed-size input signals parameter is selected.
Downsample factor is input through the port M (since R2023a)
When the output is a variable-size signal, the block maintains the phase across consecutive frames of data. For more details, see Phase Continuity.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point
Complex Number Support: Yes
Parameters
Since R2023a
Specify the downsample factor through one of these options:
Dialog parameter–– The block enables the Downsample factor, M parameter in the block dialog box.Input port–– The block enables the input port M through which you specify the downsample factor.
Specify the integer factor M by which to decrease the input sample rate.
Dependency
To enable this parameter, set
Downsample factor source to Dialog
parameter. (since R2023a)
The Sample offset (0 to M−1) parameter delays the output samples by an integer number of sample periods, D, where 0 ≤ D ≤ (M–1), so that you can select any of the M possible output phases. For example, when you downsample the sequence 1, 2, 3, ... by a factor of 4, you can select from four phases.
| Input Sequence | Sample Offset, D | Output Sequence (M = 4) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 |
|
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
The initial zero in the last three output sequences in the table is a result of the Initial conditions parameter being set to its default value of 0. See Latency for more information on the Initial conditions parameter.
When you input the downsample factor through the input port M, the Sample offset (0 to M−1) parameter is not enabled in the block dialog box. In this case, the sample offset D is automatically set to 0. (since R2023a)
Dependency
To enable this parameter, set
Downsample factor source to Dialog
parameter. (since R2023a)
Specify the method for input processing:
Columns as channels (frame based)–– When you set the Input processing parameter toColumns as channels (frame based), the block treats each of the Q input columns as an individual channel containing Pi sequential time samples. The block downsamples each channel independently by discarding M–1 rows of the input matrix following each row that it outputs.For more information, see What Is Frame-Based Processing?.
Elements as channels (sample based)–– When you set the Input processing parameter toElements as channels (sample based), the input can be a Q-D array. The Downsample block treats each element of the input as a separate channel, and resamples each channel of the input over time. The block downsamples the input array by discarding M–1 samples following each sample that it passes through to the output. The input and output sizes of the Downsample block are identical.For more information, see What Is Sample-Based Processing?.
Dependency
To enable this parameter, set
Downsample factor source to Dialog
parameter. (since R2023a)
When you set
Downsample factor source to Input
port, the Input processing
parameter is automatically set to Columns as channels
(frame based). (since R2023a)
Specify the method by which the block adjusts the rate at the output port
to accommodate the reduced number of samples. The block performs single-rate
or multirate processing depending on whether you set the Input
processing parameter to Elements as channels
(sample based) (sample-based processing mode) or
Columns as channels (frame based)
(frame-based processing mode).
Elements as channels (sample based)Enforce single-rate processingThe block forces the output sample rate to match the input sample rate (Tso = Tsi) by repeating every Mth input sample M times at the output. In this mode, the block behaves like the Sample and Hold block with a repeating trigger event of period MTsi.
Allow multirate processingThe sample period of the output is M times longer than the input sample period (Tso = MTsi).
For more details, see Sample-Based Processing
Columns as channels (frame based)Enforce single rate processingThe block generates the output at the slower (downsampled) rate using a proportionally smaller frame size than the input. The output has an upper bound size of
ceil(P/M), where P is the input frame length and M is the downsample factor. The input and output frame rates are equal. For more details, see Frame-Based Processing. For an example, see Downsample Signal in Single-Rate Frame-Based Processing Mode.Allow multirate processingThe block generates the output at the slower (downsampled) rate by using a proportionally longer frame period at the output port than at the input port. For downsampling by a factor of M, the output frame period is M times longer than the input frame period (Tfo = MTfi), but the input and output frame sizes are equal. For more details, see Frame-Based Processing. For an example, see Downsample Signal In Multirate Frame-Based Processing Mode.
Dependency
To enable this parameter, set
Downsample factor source to Dialog
parameter. (since R2023a)
When you set
Downsample factor source to Input
port, the Rate options parameter
is automatically set to Enforce single-rate
processing. (since R2023a)
Specify whether fixed-size input signals (size does not change during simulation) can have an arbitrary frame length, where the frame length does not have to be a multiple of the downsampling factor. The block uses this parameter setting only for fixed-size input signals and ignores this parameter if the input has a variable size.
When the input signal is a variable-size signal, the signal can have an arbitrary frame length, that is, the frame length does not have to be a multiple of the decimation factor.
For fixed-size input signals, if you:
Select the Allow arbitrary frame length for fixed-size input signals parameter, the frame length of the signal does not have to be a multiple of the downsampling factor. If the input is not a multiple of the downsampling factor, then the output is generally a variable-size signal. Therefore, to support an arbitrary input size, the block must also support variable-size operations, which you can enable by selecting the Allow arbitrary frame length for fixed-size input signals parameter.
Clear the Allow arbitrary frame length for fixed-size input signals parameter, the input frame length must be a multiple of the downsampling factor.
Dependency
To enable this parameter, set:
Downsample factor source to
Dialog parameter. (since R2023a)Input processing to
Columns as channels (frame based).Rate options to
Enforce single-rate processing.
The initial block value for cases of nonzero latency. You can specify a scalar or an array of the same size as the input.
Dependencies
This parameter does not appear when Input
processing is set to Columns as channels
(frame based) and Rate options is
set to Enforce single-rate processing.
Block Characteristics
Data Types |
|
Direct Feedthrough |
|
Multidimensional Signals |
|
Variable-Size Signals |
|
Zero-Crossing Detection |
|
More About
When you set the Input processing parameter to
Columns as channels (frame based) and use an input
signal of size P-by-Q, the block treats each
of the Q input columns as an individual channel containing
P sequential time samples. The block downsamples each channel
independently by discarding M–1 rows of the input matrix
following each row that it outputs.
In this mode, the block can perform either single-rate or multirate processing. You can use the Rate options parameter to specify how the block adjusts the rate at the output to accommodate the reduced number of samples.
When you set the Rate options parameter to
Enforce single-rate processing, the block generates the output at the slower (downsampled) rate using a proportionally smaller frame size than the input.The output has an upper bound size of
ceil(P/M), where P is the input frame length and M is the downsample factor.In this mode, if you input a fixed-size signal (signal dimensions do not change during simulation) and select the Allow arbitrary frame length for fixed-size input signals parameter, the input frame length can be arbitrary and does not have to be a multiple of the downsampling factor. If you clear the Allow arbitrary frame length for fixed-size input signals parameter, the input frame length must be a multiple of the downsampling factor.
In this mode, if you input a variable-size signal (signal dimensions change during simulation), the Allow arbitrary frame length for fixed-size input signals appears on the block dialog box but does not have any impact on the input frame size requirements. You can input a variable-size signal of any frame size even if you do not select the Allow arbitrary frame length for fixed-size input signals parameter.
This table summarizes the support for arbitrary input frame length when you set Input processing to
Columns as channels (frame based)and Rate options toEnforce single-rate processing.Input Signal Block Support for this Signal Support for Arbitrary Input Frame Length Input Size Output Size Fixed-size input signal Yes When you select Allow arbitrary frame length for fixed-size input signals P-by-Q Upper bound size of ceil(P/M)-by-QVariable-size input signal Yes Always P-by-Q Upper bound size of ceil(P/M)-by-QWhen you set the Rate options parameter to
Allow multirate processing, the input and output of the Downsample block are of the same size, but the sample rate of the output is M times slower than that of the input. In this mode, the block treats a P-by-Q matrix input as Q independent channels.In this mode, the block accepts only fixed-size signals and these signals can have an arbitrary frame length.
This table summarizes the support for arbitrary input frame length when you set Input processing to
Columns as channels (frame based)and Rate options toAllow multirate processing.Input Signal Block Support for this Signal Support for Arbitrary Input Frame Length Input Size Output Size Fixed-size input signal Yes Always P-by-Q P-by-Q Variable-size input signal No Not applicable Not applicable Not applicable
When you set the Input processing parameter to
Columns as channels (frame based) and Rate
options parameter to Enforce single-rate
processing, under certain conditions, the
Downsample block maintains the phase across consecutive frames of
data.

| Input Conditions | Downsample Factor Source | Support for Arbitrary Input Frame Length | Output Signal | Phase Continuity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed-size input signal | Specify in block dialog box | When you select Allow arbitrary frame length for fixed-size input signals | Variable-size signal | Yes |
| Variable-size input signal | Specify in block dialog box | Always | Variable-size signal | Yes |
Fixed-size or variable-size input signal | Specify through input port Downsample factor does not change during simulation | –– | Variable-size signal | Yes |
Under certain conditions, the phase resets to 0 and is not maintained across consecutive frames of data.
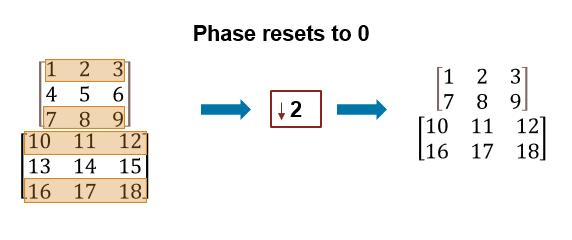
| Input Conditions | Downsample Factor Source | Support for Arbitrary Input Frame Length | Output Signal | Phase Continuity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed-size input signal | Specify in block dialog box | When you clear Allow arbitrary frame length for fixed-size input signals | Fixed-size signal | Phase is always 0 |
Fixed-size or variable-size input signal | Specify through input port At the event when downsample factor changes during simulation | –– | Variable-size signal | Phase resets to 0 |
When you set the Input processing parameter to
Elements as channels (sample based), the block treats
a P-by-Q matrix input as
P*Q independent channels, and resamples
each channel over time. The output sample period
(Tso) is M
times longer than the input sample period
(Tso =
M*Tsi), and the input and output
sizes are identical.
In this mode, the block accepts only fixed-size signals and these signals can have an arbitrary frame length.
This table summarizes the support for arbitrary input frame length when you set
Input processing to Elements as channels
(sample based).
| Input Signal | Block Support for this Signal | Support for Arbitrary Input Frame Length | Input Size | Output Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed-size input signal | Yes | Always | P-by-Q | P-by-Q |
| Variable-size input signal | No | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable |
Latency is the delay, measured in samples or frames, between the input and the output of the block.
The Downsample block has zero-tasking latency in the following cases:
The downsample factor M is
1.The Input processing parameter is set to
Columns as channels (frame based), and the Rate options parameter is set toEnforce single-rate processing.The Input processing parameter is set to
Columns as channels (frame based), the Rate options parameter is set toAllow multirate processing, the Sample offset (0 to M−1) parameter D is set to0, and the input frame size is equal to 1.The Input processing parameter is set to
Elements as channels (sample based), and the Sample offset (0 to M−1) parameter D is0.
Zero-tasking latency means that the block propagates input sample D+1 (received at t = 0) as the first output sample, followed by input sample D+1+M, input sample D+1+2M, and so on. When there is zero-tasking latency, the block ignores the value of the Initial conditions parameter.
In all other cases, the latency is nonzero:
When the Input processing parameter is set to
Elements as channels (sample based), the latency is one sample.When the Input processing parameter is set to
Columns as channels (frame based)and the input frame size is greater than one, the latency is one frame.
In all cases of one-sample latency, the initial condition for each channel appears as the first output sample. Input sample D+1 appears as the second output sample for each channel, followed by input sample D+1+M, input sample D+1+2M, and so on. The Initial conditions parameter can be an array of the same size as the input or a scalar to be applied to all signal channels.
In all cases of one-frame latency, the Pi rows of the initial condition matrix appear in sequence as the first Pi output rows. Input sample D+1 (row D+1 of the input matrix) appears in the output as sample Pi+1, followed by input sample D+1+M, input sample D+1+2M, and so on. The Initial conditions value can be an Pi-by-Q matrix containing one value for each channel or a scalar to be repeated across all elements of the Pi-by-Q matrix.
Note
For more information on latency and the Simulink® tasking modes, see Excess Algorithmic Delay (Tasking Latency) and Time-Based Scheduling and Code Generation (Simulink Coder).
Extended Capabilities
Generated code relies on the memcpy or
memset function (string.h) under certain
conditions.
HDL Coder™ provides additional configuration options that affect HDL implementation and synthesized logic.
It is good practice to follow the Downsample block with a unit delay. Doing so prevents the code generator from inserting an extra bypass register in the HDL code.
See also Multirate Model Requirements for HDL Code Generation (HDL Coder).
This block has one default HDL architecture.
| ConstrainedOutputPipeline | Number of registers to place at
the outputs by moving existing delays within your design. Distributed
pipelining does not redistribute these registers. The default is
|
| InputPipeline | Number of input pipeline stages
to insert in the generated code. Distributed pipelining and constrained
output pipelining can move these registers. The default is
|
| OutputPipeline | Number of output pipeline stages
to insert in the generated code. Distributed pipelining and constrained
output pipelining can move these registers. The default is
|
This block supports code generation for complex signals.
Input processing set to
Columns as channels (frame based)is not supported.For Input processing set to
Elements as channels (sample based), selectAllow multirate processing. With this setting, if Sample offset is set to 0, Initial conditions has no effect on generated code.
Version History
Introduced before R2006aYou can now specify the downsample factor through an input port when the Downsample block operates in the single-rate frame-based processing mode. When you specify the downsample factor through the input port, you can change the factor during simulation.
Starting in R2022b, this block supports input signals with arbitrary frame lengths when the:
Input signal is a fixed-size signal (signal dimensions do not change during simulation) and the block allows for multirate processing
Input signal is a fixed-size signal, block enforces single-rate processing, and you select the Allow arbitrary frame length for fixed-size input signals parameter (if enabled)
Input signal is a variable-size signal (signal dimensions change during simulation)
When this block supports an arbitrary frame length input signal, the input frame length does not have to be a multiple of the downsampling factor.
For more details, see Frame-Based Processing and Sample-Based Processing.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleccione un país/idioma
Seleccione un país/idioma para obtener contenido traducido, si está disponible, y ver eventos y ofertas de productos y servicios locales. Según su ubicación geográfica, recomendamos que seleccione: .
También puede seleccionar uno de estos países/idiomas:
Cómo obtener el mejor rendimiento
Seleccione China (en idioma chino o inglés) para obtener el mejor rendimiento. Los sitios web de otros países no están optimizados para ser accedidos desde su ubicación geográfica.
América
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)
