Flow and Pressure Control
In this section, you can find examples of flow control systems in multiple Simscape Fluids domains.
Featured Examples
2-Position Valve Actuator
Demonstrates the Multiposition Valve Actuator block with two positions. The same signal controls two valve actuators, but the actuators use different values of the Switching-on time, Switching-off time, and Initial position parameters.
3-Position Valve Actuator
The behavior of three different Multiposition Valve Actuator blocks. In each block Actuator positions is 3. All three actuators are driven by the same pulse signals. The values of the Push-pin stroke, Switching-on time and Switching-off time parameters of the three actuators are different, which illustrates the parameter impact.
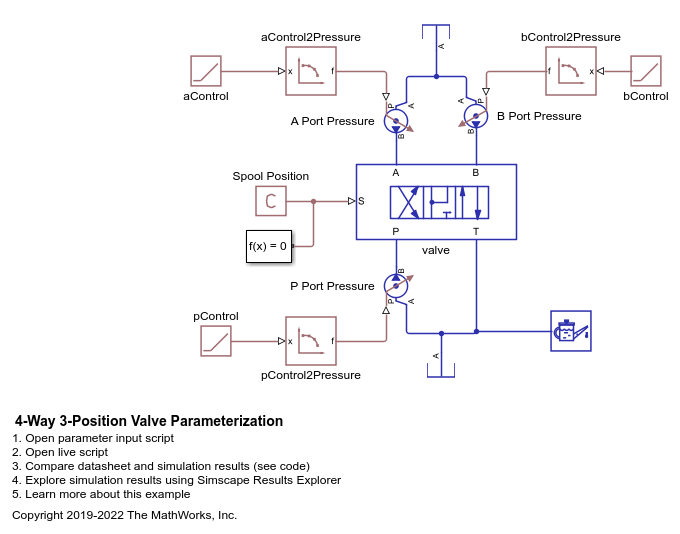
4-Way 3-Position Valve Parameterization
Parameterize and test a 4-way 3-position valve with a test harness. A plot script is provided with the example for comparing output flow between the block and data to verify the test harness. A live script is also provided with this example to explain the parameterization and the test harness workflow in detail.
4-Way Directional Valve with Mechanical Effects
Compares two 4-way directional valves, one with mechanical components to account for spool mass, valve spring and damper and one without (ideal valve). The input force to both valves is a sine wave. The operation of two valves are compared for different displacement frequencies, valve spring stiffness and damper coefficients.
Flow Divider
A simple way of modeling of the flow divider and using it with the load harness. The flow divider helps in dividing the input flow in desired percentage when the loads connected to the two lines are unequal. Flow divider allows flow only in forward direction. Therefore when it is used with the loads where unloading is done through reverse flows, then it should be used in conjunction with the direction control valves.
Hydraulic Actuator with Dual Counterbalance Valves
An actuator controlled by a 4-way directional valve and loaded with an overriding load, requiring the use of counterbalance valves to prevent the load from creeping when the directional valve is in the neutral position. In the neutral position, the directional valve connects ports A and B to the reservoir while blocking the pressure port P. The counterbalance valves block flow from returning to the reservoir, thus holding the actuator in place.
Hydraulic Actuator with Dual Counterbalance Valves
Warning: This example uses the hydraulic domain, which will be removed in a future release. Find an equivalent example model that uses the isothermal liquid domain here: Hydraulic Actuator with Dual Counterbalance Valves. To convert models to the isothermal liquid domain, use the hydraulicToIsothermalLiquid tool.
Hydraulic Flapper-Nozzle Amplifier
An amplifier that consists of two fixed orifices, two variable orifices representing nozzles, flapper, and main valve simulated with mass, viscous friction, and centering spring. A double-acting actuator represents a hydraulic servo actuator connected to both sides of the main valve. A feedback spring connects the flapper and the main valve.
Hydraulic Flow Rectifier Circuit
A flow rectifier circuit with four check valves and a flow control valve. It is used to allow a single flow control valve to control fluid flow in both directions. Similar to a Graetz circuit implemented with diodes, the check valves are arranged in such a way that flow always passes through the flow control valve in the same direction. In the Orifices subsystem, there are two more check valves that are used to select the orifice that the flow passes through depending on the flow direction.
Hydraulic Flow Rectifier Circuit
Warning: This example uses the hydraulic domain, which will be removed in a future release. Find an equivalent example model that uses the isothermal liquid domain here: Hydraulic Flow Rectifier Circuit. To convert models to the isothermal liquid domain, use the hydraulicToIsothermalLiquid tool.
Position Control Servo Valve
Model, parameterize, and test a position control servo valve with a closed loop control. When you run the model, it generates a comparison plot between the commanded and the achieved position in the actuator with respect to the time. A position control servo valve provides a precise and fast control of the position in the actuator with a very small electrical signal to the torque motor. Aerospace, construction and agricultural equipments manufacturers use these valves for safety critical applications.
Pressure Control Solenoid
Model, parameterize, and test a pressure control solenoid valve. This example also generates a plot of the relationship between applied solenoid force and the resulting actuator port pressure.
Pressure Reducing Valve in Punching Operation
Models a hydraulic system with a direct operated, pressure reducing valve. This system helps to limit and maintain pressure in a hydraulic punching machine. Pressure reducing valves are common in hydraulic pressing, drilling, and stamping applications.
Optimize Pressure Reducing Valve Model for Real-Time Simulation
Identify simulation slowdowns, resolve performance issues, and configure a Simscape Fluids™ model for real-time simulation. This example uses the Pressure Reducing Valve In Punching Operation model, PressureReducingValveInPunchingOperation which is called here as the original model. In this example, you measure the simulation time, identify the factors that affect simulation speed, optimize the model, and prepare the model for code generation.
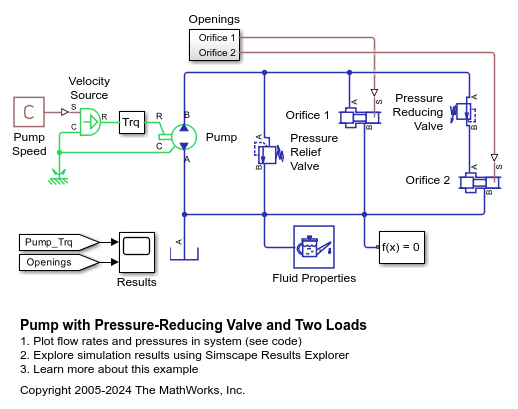
Pump with Pressure-Reducing Valve and Two Loads
A power unit consisting of a fixed-displacement pump, constant angular velocity source, pressure relief valve, pressure-reducing valve, and two variable orifices. The two variable orifices simulate fluid consumption in the main branch and in the reduced pressure branch, respectively.
Priority Valve Controlling Two Hydraulic Motors
A pressure-compensated 3-way flow control valve. This valve maintains constant flow rate through the main hydraulic motor, which is connected to the pressure-compensated outlet of the flow control valve. It acts as a priority valve, diverting the excess flow to the auxiliary hydraulic motor if the main hydraulic motor receives enough fluid to maintain a preset angular velocity. The auxiliary motor is shut off completely if there is insufficient flow to power the main hydraulic motor.
Priority Valve Controlling Two Hydraulic Motors
Warning: This example uses the hydraulic domain, which will be removed in a future release. Find an equivalent example model that uses the isothermal liquid domain here: Priority Valve Controlling Two Hydraulic Motors. To convert models to the isothermal liquid domain, use the hydraulicToIsothermalLiquid tool.
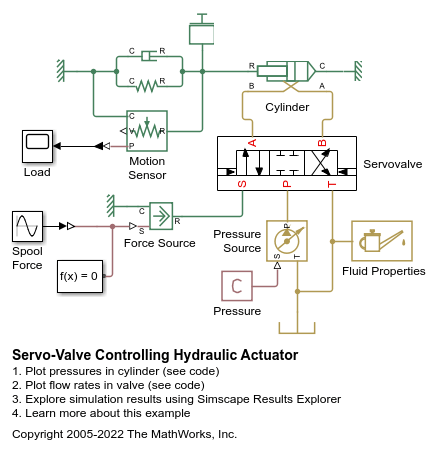
Servo-Valve Controlling Hydraulic Actuator
Warning: This example uses the hydraulic domain, which will be removed in a future release. Find an equivalent example model that uses the isothermal liquid domain here: Servo Valve with Custom Fidelity. To convert models to the isothermal liquid domain, use the hydraulicToIsothermalLiquid tool.
Servo Valve with Custom Fidelity
Compares the mechanical performance of various spool actuation configurations and model fidelity levels for a hydraulic 4-way 3-position directional valve. The directional valve controls a simple double-acting cylinder in a closed-loop application. This example allows you to choose among four different spool actuation designs:
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleccione un país/idioma
Seleccione un país/idioma para obtener contenido traducido, si está disponible, y ver eventos y ofertas de productos y servicios locales. Según su ubicación geográfica, recomendamos que seleccione: .
También puede seleccionar uno de estos países/idiomas:
Cómo obtener el mejor rendimiento
Seleccione China (en idioma chino o inglés) para obtener el mejor rendimiento. Los sitios web de otros países no están optimizados para ser accedidos desde su ubicación geográfica.
América
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)