geocode
Syntax
Description
Use Online Provider and Installed List of Placenames
geocodedGT = geocode(name)
The function geocodes the specified placename by using an online provider and an
installed list of world regions, US states, and world cities. For more information about
how geocode uses the online provider and the installed list, see
Algorithms.
geocodedGT = geocode(name,adminlevel)
Use Custom Table of Placenames
geocodedGT = geocode(name,customNamesGT)name table variable. If the table does not have a
name table variable, then the function searches the second table
variable.
geocodedGT = geocode(name,customNamesGT,namevar)
Additional Options
geocodedGT = geocode(___,Name=Value)FilterResults name-value argument.
Examples
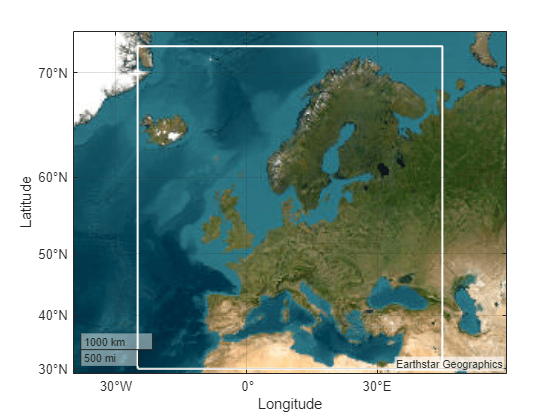
Geocode the world region of Europe. The output is a geospatial table that contains the geocoded placename, a shape object associated with the geocoded placename, and the administrative level of the geocoded placename.
geocodedGT = geocode("Europe")geocodedGT=1×3 table
Shape Name AdminLevel
____________ ________ __________
geopolyshape "Europe" "region"
When you geocode the name of a world region, the shape object is an area of interest (AOI) that represents either an outline or a quadrangle that approximates the region. Display the boundary of the AOI on a map. Provide more geographic context for the AOI by zooming out.
figure geobasemap topographic geoplot(geocodedGT,LineWidth=2,EdgeColor="#7E2F8E",FaceColor="none") geolimits([15 75],[-54 75])
Specify placenames for the states that comprise New England: Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Connecticut, and Rhode Island. Then, geocode the placenames. The output is a geospatial table that contains the geocoded placenames, the shape objects associated with the placenames, and the administrative levels of the placenames.
names = ["Maine","New Hampshire","Vermont","Massachusetts","Connecticut","Rhode Island"]; geocodedGT = geocode(names,"state")
geocodedGT=6×3 table
Shape Name AdminLevel
____________ _______________ __________
geopolyshape "Maine" "state"
geopolyshape "New Hampshire" "state"
geopolyshape "Vermont" "state"
geopolyshape "Massachusetts" "state"
geopolyshape "Connecticut" "state"
geopolyshape "Rhode Island" "state"
When you geocode the names of US states, the shape objects are AOIs that represent the outlines of the states. Display the AOIs on a map.
figure
geobasemap none
geoplot(geocodedGT)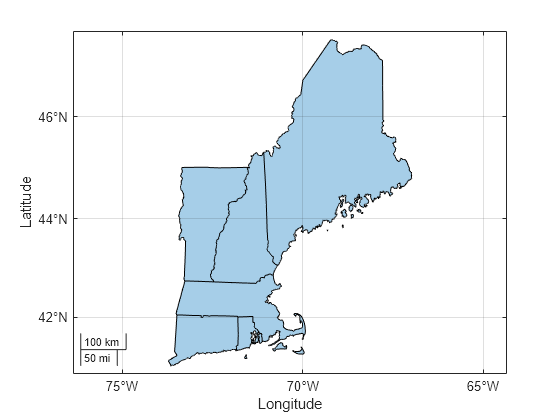
Since R2025a
Geocode the placename Essex using the county administrative level. The output is geospatial table that contains several matches for the placename, including Essex County in Massachusetts.
GT1 = geocode("Essex","county")
GT1=6×3 table
Shape Name AdminLevel
____________ _______________________ __________
geopolyshape "Essex, England, GBR" "county"
geopolyshape "Essex County, MA, USA" "county"
geopolyshape "Essex County, NJ, USA" "county"
geopolyshape "Essex County, NY, USA" "county"
geopolyshape "Essex County, VT, USA" "county"
geopolyshape "Essex County, VA, USA" "county"
Create a new geospatial table that contains only the result for Massachusetts.
GT2 = geocode("Essex County, MA","county")
GT2=1×3 table
Shape Name AdminLevel
____________ _______________________ __________
geopolyshape "Essex County, MA, USA" "county"
When you geocode the name of a county, the Shape variable of the table is an AOI that approximates the region. Display the AOI on a map.
figure
geobasemap streets
geoplot(GT2)
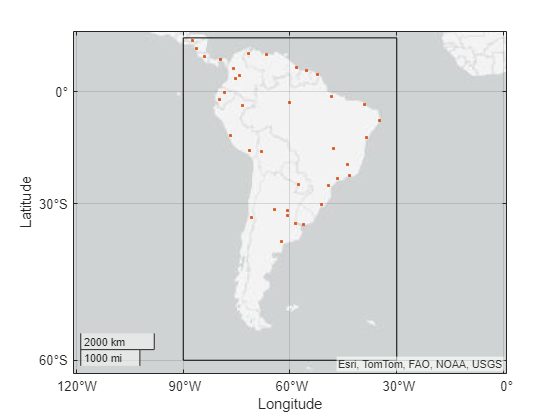
Geocode all the world cities in the installed list of placenames. Then, clip the cities to an AOI.
Get the names of world cities in the installed list by using the placenames function.
names = placenames("city");Geocode the placenames. When you specify multiple placenames and the "city" administrative level, the geocode function searches the installed list of placenames instead of using the online provider.
geocodedGT = geocode(names,"city");View the first eight rows of the output table. When you geocode the names of cities, the shape objects in the output table are points that represent the city locations.
head(geocodedGT)
Shape Name AdminLevel
_______________________ _____________ __________
( 5.2985°N, 3.9509°W) "Abidjan" "city"
(24.6525°N, 54.7589°E) "Abu Dhabi" "city"
( 5.6106°N, 0.2121°W) "Accra" "city"
(37.0613°N, 35.3894°E) "Adana" "city"
( 9.0235°N, 38.7575°E) "Addis Ababa" "city"
(34.6645°S, 138.8528°E) "Adelaide" "city"
(12.8767°N, 44.5408°E) "Aden" "city"
(22.7778°N, 72.2474°E) "Ahmadabad" "city"
Prepare to clip the world cities by extracting the points from the table.
points = geocodedGT.Shape;
Get an AOI that represents a bounding box for South America. Then, clip the world cities to the AOI. For more information about clipping shapes to AOIs, see Clip Vector Data to Area of Interest.
GT = geocode("South America");
aoi = GT.Shape;
clipped = geoclip(points,aoi);Display the AOI and the clipped cities on a map.
figure geoplot(aoi,FaceColor="none") hold on geoplot(clipped)
Since R2025a
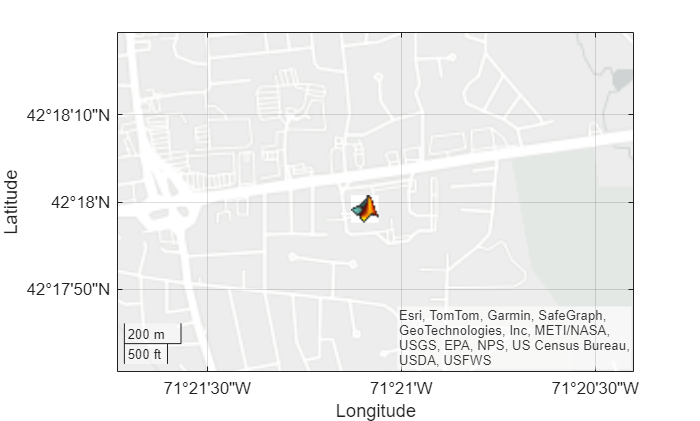
Geocode the address of the MathWorks Apple Hill campus.
geocodedGT = geocode("1 Apple Hill Drive, Natick, MA","address")
geocodedGT=1×3 table
Shape Name AdminLevel
______________________ ____________________________________________ __________
(42.2998°N, 71.3516°W) "1 Apple Hill Drive, Natick, MA, 01760, USA" "address"
When you geocode an address, the output table contains a point shape in geographic coordinates. Display an icon at the coordinates stored in the point shape.
lat = geocodedGT.Shape.Latitude;
lon = geocodedGT.Shape.Longitude;
geoiconchart(lat,lon,"matlabicon.gif")Zoom in by changing the geographic limits.
geolimits([42.2946 42.3054],[-71.3622 -71.34])
Since R2025a
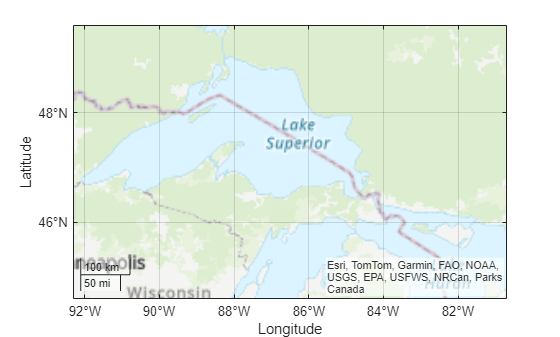
Geocode the placename Lake Superior, MI using the administrative level for physical features.
geocodedGT = geocode("Lake Superior, MI","physical")
geocodedGT=1×3 table
Shape Name AdminLevel
____________ ________________________ __________
geopolyshape "Lake Superior, MI, USA" "physical"
When you geocode the name of a physical feature, the Shape variable of the table contains an AOI that represents a quadrangle. View a map of the region by plotting the AOI with no face or edge color.
figure geobasemap topographic geoplot(geocodedGT,FaceColor="none",EdgeColor="none")
Create a custom table of placenames by reading data from a file. Then, use the custom table to geocode a specified placename.
Create the custom table by reading data from a shapefile that contains placenames in Boston. The table stores the placenames in the NAME variable and the locations of the placenames in the Shape variable.
customNamesGT = readgeotable("boston_placenames.shp")customNamesGT=13×4 table
Shape NAME FEATURE COORD
______________________ ____________________ _____________ _________________
(234028.23, 900038.00) "'BACK BAY'" "PPL-SUBDVSN" "422100N0710515W"
(233569.77, 900190.06) "BACK BAY FENS" "MARSH" "422105N0710535W"
(235739.28, 901126.44) "BEACON HILL" "HILL" "422135N0710400W"
(236266.39, 900974.88) "BOSTON" "PPL" "422130N0710337W"
(235743.22, 900355.06) "BOSTON NECK" "PENINSULA" "422110N0710400W"
(234685.09, 901429.69) "BROAD CANAL" "CANAL" "422145N0710446W"
(232989.64, 901884.31) "CAMBRIDGE" "PPL" "422200N0710600W"
(236536.17, 901901.88) "COPPS HILL" "HILL" "422200N0710325W"
(234591.28, 901892.00) "'EAST CAMBRIDGE'" "PPL-SUBDVSN" "422200N0710450W"
(235741.66, 900663.62) "FLAGSTAFF HILL" "HILL" "422120N0710400W"
(237114.73, 900670.75) "FORT POINT CHANNEL" "CHANNEL" "422120N0710300W"
(235741.31, 900725.31) "FROG POND" "LAKE" "422122N0710400W"
(236548.23, 899587.88) "SOUTH BAY" "INLET" "422045N0710325W"
Specify the placenames of two hills in Boston. Then, geocode the placenames by searching the custom table. By default, the geocode function searches for the placenames using the NAME variable of the custom table.
names = ["BEACON HILL","COPPS HILL"]; geocodedGT = geocode(names,customNamesGT);
View the output table. When you pass a custom table of placenames to the geocode function, the output table is a subset of the input table.
geocodedGT
geocodedGT=2×4 table
Shape NAME FEATURE COORD
______________________ _____________ _______ _________________
(235739.28, 901126.44) "BEACON HILL" "HILL" "422135N0710400W"
(236536.17, 901901.88) "COPPS HILL" "HILL" "422200N0710325W"
Create a custom table of placenames by reading data from a file. Then, geocode a specified placename by searching the specified table variable of placenames.
Create the custom table by reading data from a shapefile that contains tsunami events. The table stores the placenames in the Location variable and the shape objects in the Shape variable.
customNamesGT = readgeotable("tsunamis.shp",CoordinateSystemType="geographic"); head(customNamesGT)
Shape Year Month Day Hour Minute Second Val_Code Validity Cause_Code Cause Eq_Mag Country Location Max_Height Iida_Mag Intensity Num_Deaths Desc_Deaths
_______________________ ____ _____ ___ ____ ______ ______ ________ _______________________ __________ ________________ ______ _________________ ________________________ __________ ________ _________ __________ ___________
( 3.8000°S, 128.3000°E) 1950 10 8 3 23 NaN 2 "questionable tsunami" 1 "Earthquake" 7.6 "INDONESIA" "JAVA TRENCH, INDONESIA" 2.8 1.5 1.5 0 0
(19.5000°N, 156.0000°W) 1951 8 21 10 57 NaN 4 "definite tsunami" 1 "Earthquake" 6.9 "USA" "HAWAII" 3.6 1.8 NaN 0 0
( 9.0200°S, 157.9500°E) 1951 12 22 0 0 NaN 2 "questionable tsunami" 6 "Volcano" NaN "SOLOMON ISLANDS" "KAVACHI" 6 2.6 NaN 0 0
(42.1500°N, 143.8500°E) 1952 3 4 1 22 41 4 "definite tsunami" 1 "Earthquake" 8.1 "JAPAN" "SE. HOKKAIDO ISLAND" 6.5 2.7 2 33 1
(19.1000°N, 155.0000°W) 1952 3 17 3 58 NaN 4 "definite tsunami" 1 "Earthquake" 4.5 "USA" "HAWAII" 1 NaN NaN 0 0
(43.1000°N, 82.4000°W) 1952 5 6 0 0 NaN 1 "very doubtful tsunami" 9 "Meteorological" NaN "USA" "LAKE HURON, MI" 1.52 NaN NaN 0 0
(52.7500°N, 159.5000°E) 1952 11 4 16 58 NaN 4 "definite tsunami" 1 "Earthquake" 9 "RUSSIA" "KAMCHATKA" 18 4.2 4 2236 3
(50.0000°N, 156.5000°E) 1953 3 18 0 0 NaN 3 "probable tsunami" 1 "Earthquake" 5.8 "RUSSIA" "N. KURIL ISLANDS" 1.5 0.6 NaN 0 0
Geocode the placename Hawaii by searching the custom table. Specify the table variable containing the placenames as Location.
name = "Hawaii"; geocodedGT = geocode(name,customNamesGT,"Location");
View the output table. When you pass a custom table of placenames to the geocode function, the output table is a subset of the input table.
geocodedGT
geocodedGT=3×19 table
Shape Year Month Day Hour Minute Second Val_Code Validity Cause_Code Cause Eq_Mag Country Location Max_Height Iida_Mag Intensity Num_Deaths Desc_Deaths
_______________________ ____ _____ ___ ____ ______ ______ ________ __________________ __________ __________________________ ______ _______ ________ __________ ________ _________ __________ ___________
(19.5000°N, 156.0000°W) 1951 8 21 10 57 NaN 4 "definite tsunami" 1 "Earthquake" 6.9 "USA" "HAWAII" 3.6 1.8 NaN 0 0
(19.1000°N, 155.0000°W) 1952 3 17 3 58 NaN 4 "definite tsunami" 1 "Earthquake" 4.5 "USA" "HAWAII" 1 NaN NaN 0 0
(19.3340°N, 155.0240°W) 1975 11 29 14 47 40.4 4 "definite tsunami" 3 "Earthquake and Landslide" 7.1 "USA" "HAWAII" 14.3 3 3 2 1
Since R2025a
In many cases, the geocode function finds multiple matches for a specified placename. To return the first match, specify the FilterResults argument as "first".
Geocode the placename Essex using the county administrative level. Include only the first result in the output table.
geocodedGT = geocode("Essex","county",FilterResults="first")
geocodedGT=1×3 table
Shape Name AdminLevel
____________ _____________________ __________
geopolyshape "Essex, England, GBR" "county"
Since R2025a
When you do not specify an administrative level, the geocode function searches the administrative levels in this order: "region", "state", "country", "city", "address", and "physical". By default, the function returns results for one administrative level, which is the first administrative level with matches. To return results for all the administrative levels, specify the FilterResults argument as "none".
Geocode the placename Pacific and return results for all the administrative levels.
geocodedGT = geocode("Pacific",FilterResults="none")
geocodedGT=9×3 table
Shape Name AdminLevel
_____________ _________________________ __________
geopolyshape "Pacific" "region"
geopolyshape "Pacific Ocean" "region"
geopolyshape "Pacific County, WA, USA" "county"
geopointshape "Pacific, MO, USA" "city"
geopointshape "Pacific, WA, USA" "city"
geopointshape "Pacific, WI, USA" "city"
geopointshape "Pacific, NC, USA" "city"
geopointshape "Pacific, CA, USA" "city"
geopolyshape "Pacific, BC, CAN" "physical"
The output table contains matches for regions, counties, cities, and physical features. The function did not find matches for the state or address administrative levels.
Since R2025a
By default, the geocode function filters results from the online provider by applying partial string matching of leading characters. You can view unfiltered results from the online provider by specifying the PartialMatching name-value argument as false.
Geocode the placename Mount Fuji using the administrative level for physical features. By default, the function filters the results.
filteredGT = geocode("Mount Fuji","physical")
filteredGT=1×3 table
Shape Name AdminLevel
____________ _________________ __________
geopolyshape "Mount Fuji, JPN" "physical"
Geocode the placename again. This time, return the unfiltered results. The geospatial table contains additional results from the online provider.
unfilteredGT = geocode("Mount Fuji","physical",PartialMatch=false)
unfilteredGT=9×3 table
Shape Name AdminLevel
____________ ___________________________________________ __________
geopolyshape "Mount Fuji, JPN" "physical"
geopolyshape "Mt. Fuji, Hidaka, Saitama, JPN" "physical"
geopolyshape "Mt. Fuji, Minokamo, Gifu, JPN" "physical"
geopolyshape "Mt. Fuji, Nasushiobara, Tochigi, JPN" "physical"
geopolyshape "Mt. Fuji, Yokosuka, Kanagawa, JPN" "physical"
geopolyshape "Mt. Fuji, Nishiaizu, Yama, Fukushima, JPN" "physical"
geopolyshape "Mt. Fuji, Kasama, Ibaraki, JPN" "physical"
geopolyshape "Mt. Fuji, Ueda, Nagano, JPN" "physical"
geopolyshape "Mt. Fuji, Gotemba, Shizuoka, JPN" "physical"
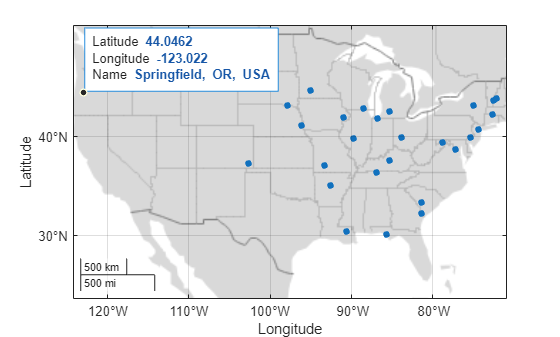
Explore geocoded placenames on a map using custom data tips.
Geocode the placename Springfield using the city administrative level. Create a subtable of cities in the conterminous United States. The table stores the geocoded cities using point shapes in geographic coordinates.
cities = geocode("Springfield","city"); us = geocode("United States (conterminous)"); idx = isinterior(us.Shape,cities.Shape); citiesInUS = cities(idx,:);
Display the cities on a map. Prepare to add data tips to the points by storing the Point object in pt.
figure
geobasemap grayland
pt = geoplot(citiesInUS,MarkerSize=15);Add the geocoded placenames to the data tip template. For more information about creating custom data tips, see Add Data Tips to Point, Line, and Polygon Shapes.
dtRow = dataTipTextRow("Name",citiesInUS.Name);
pt.DataTipTemplate.DataTipRows(end+1) = dtRow;Create a data tip by using the datatip function, the Point object, and the geographic coordinates of a city. You can also add data tips by pausing on, clicking, or tapping the points.
dt = datatip(pt,44,-123);
Input Arguments
Placenames, specified as a string scalar, a vector of strings, a character vector, or a cell array of character vectors.
To use the online provider, you must specify this argument as a string scalar or a
character vector. For more information about when the geocode
function uses the online provider, see Algorithms.
Administrative level, specified as one of these options.
| Option | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
"region" | World regions, including continents and oceans |
|
"state" | States and provinces |
|
"county" (since R2025a) | Counties |
|
"city" | Cities |
|
"address" (since R2025a) | Street addresses and postal codes |
|
"physical" (since R2025a) | Land and water features |
|
To return results for multiple administrative levels, specify the
FilterResults name-value argument as "none"
and do not specify a value for adminlevel.
The geocode function searches the administrative levels using
the online provider and the installed list of placenames. For more information about the
search algorithm for each administrative level, see Algorithms.
Custom placenames and shapes, specified as a geospatial table. For more information about geospatial tables, see Create Geospatial Tables.
customNamesGT must contain these table variables:
A
Shapevariable that specifies the point, line, or polygon shapes.A variable that specifies the custom placenames. This variable must contain text data.
By default, the function searches for the specified placenames using the
case-insensitive name table variable. If the table does not have a
name variable, or has more than one name
variable, then the function uses the second table variable. You can specify which table
variable to search by using the namevar argument.
Table variable containing the custom placenames, specified using one of these indexing schemes. The table variable must contain text data.
| Indexing Scheme | Examples |
|---|---|
Variable name:
|
|
Variable index:
|
|
Variable type:
|
|
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: geocode(name,FilterResults="first") returns the first
result.
Since R2025a
How to filter results, specified as "auto",
"first", or "none". The behavior of
FilterResults depends on whether you use the online provider
and installed list of placenames or specify a custom table of
placenames.
| Online Provider and Installed List | Custom Table |
|---|---|
Each option searches the administrative levels using the algorithm described in Algorithms.
| Each option searches for the specified placename and filters the
results by applying the
|
Option to use partial string matching, specified as a numeric or logical
1 (true) or 0
(false). The behavior of PartialMatch
depends on whether the function finds results using the installed list, a custom
table, or the online provider.
| Option | Installed List or Custom Table | Online Provider |
|---|---|---|
true | Enable partial string matching of leading characters. For example,
| After obtaining results from the online provider, filter the results by applying partial string matching of leading characters. For example, the result of
The function applies partial string
matching when |
false | Do not enable partial string matching. This option requires you to specify placenames that are exact matches for placenames in the installed list. For example,
| Do not use partial string matching to filter results from the online provider. For example, the result of
|
Option to ignore case, specified as a numeric or logical 1
(true) or 0 (false).
true— Ignore case.false— Do not ignore case.
Output Arguments
Geocoded placenames and shapes, returned as a geospatial table.
When you use the online provider and installed list of placenames, the geospatial table contains three variables:
Shape— Shape of the geocoded placename, returned as ageopolyshapeorgeopointshapeobject. The type of object depends on the administrative level of the geocoded placename.When the administrative level is
"region"or"state", the shape is ageopolyshapeobject that represents either an outline or a quadrangle that approximates the region. Quadrangles can cover a different area than the outline of the region.When the administrative level is
"county"or"physical", the shape is ageopolyshapeobject that represents a quadrangle that approximates the region. Quadrangles can cover a different area than the outline of the region.When the administrative level is
"city"or"address", the shape is ageopointshapeobject that represents the location of the city or address.
Name— Geocoded placename, returned as a string scalar.AdminLevel— Administrative level, returned as"region","state","county","city","address", or"physical".
When you use the online provider and installed list of placenames, the geospatial table has a maximum of 50 rows.
When you use a custom table of placenames by specifying the
customNamesGT argument, the output geospatial table is a subset
of the custom table. As a result, the output geospatial table has the same table
variables as the custom table.
Limitations
When the geocode function uses the online provider, deployment using
MATLAB®
Compiler™ is not supported. For information about when the function uses the online
provider, see Algorithms.
More About
Geocoding is the process of converting addresses
or other locations into geographic coordinates. The geocode function
represents geocoded placenames using point, line, and polygon shape objects.
Tips
The online provider updates the data periodically. As a result, the
geocodefunction can return different results over time.In offline environments:
Geocoding the names of regions, states, and cities is limited to the installed list of placenames. You can query the installed list by using the
placenamesfunction.Geocoding the names of counties, addresses, and physical features is not supported.
Algorithms
When you do not specify the adminlevel argument, the
geocode function searches the administrative levels in this order:
"region", "state", "county",
"city", "address", and
"physical".
The function uses a different search algorithm for each administrative level. This table describes the search algorithm for each administrative level.
| Administrative Level | Search Algorithm |
|---|---|
"region" | The algorithm depends on the number of placenames in
|
"state" | The algorithm depends on the number of placenames in
|
"county" | Use the online provider. |
"city" | The algorithm depends on the number of placenames in
|
"address" | Use the online provider. |
"physical" | Use the online provider. |
You can query the installed list of placenames by using the placenames
function.
By default, the function returns results for the first administrative level that
contains matches for the placename. To specify the administrative level, use the
adminlevel argument. To return results for multiple administrative
levels, use the FilterResults name-value argument.
Version History
Introduced in R2024bThe geocode function uses an online provider in addition to the
installed list of placenames. As a result, you can geocode the names of street addresses,
provinces, counties, and land or water features. You can also geocode the names of
additional regions, states, and cities.
Depending on the specified placename and administrative level, the
geocode function uses only the online provider and does not search
the installed database of placenames. As a result, the geocode function
can return different values in R2025a compared to previous releases.
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleccione un país/idioma
Seleccione un país/idioma para obtener contenido traducido, si está disponible, y ver eventos y ofertas de productos y servicios locales. Según su ubicación geográfica, recomendamos que seleccione: .
También puede seleccionar uno de estos países/idiomas:
Cómo obtener el mejor rendimiento
Seleccione China (en idioma chino o inglés) para obtener el mejor rendimiento. Los sitios web de otros países no están optimizados para ser accedidos desde su ubicación geográfica.
América
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)