sltrace
Analyze structure of model by tracing signal sources and destinations
Since R2021b
Description
g = sltrace(p)p and returns the traced signal path
information as the sltrace.Graph
object g.
When the specified port is a block input port, the function traces the signal to the first nonvirtual source block.
When the specified port is a block output port, the function traces the signal to the first nonvirtual destination block.
g = sltrace(___,Name=Value)TraceAll
argument as on, the function traces a signal to all source or destination
blocks.
Examples
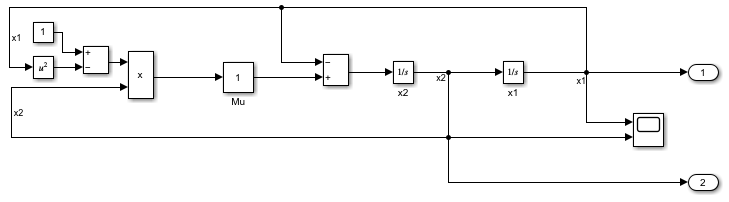
The model for this example implements the second-order differential Van der Pol (vdp) equation.
,
where represents damping in the system.
Open the model vdp. In the model, the signal x1 represents the first derivative of . The signal x2 represents the second derivative of .
mdl = "vdp";
open_system(mdl)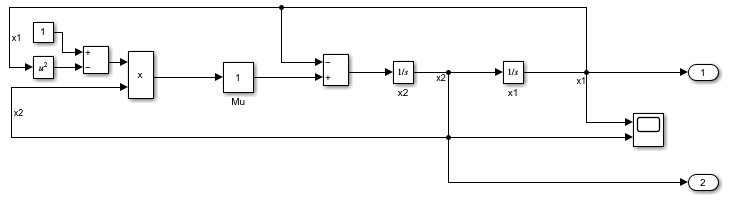
Use the sltrace function to trace all source blocks for the signal x2, which is the input signal for the Integrator block named x1.
x2Sources = sltrace((mdl + "/x1"),"Source",Port=1,TraceAll="on");
When you trace all sources for a signal, the sltrace.Graph object that the sltrace function returns contains information about more than just the blocks that produce the input signals for the specified block. The sltrace.Graph object contains information for all blocks that produce output values that affect the value of the signal you trace.
length(x2Sources.SrcBlocks)
ans = 10
To see the signal path in the block diagram, use the highlight function to highlight all the source blocks in the sltrace.Graph object x2Sources. The source blocks in the sltrace.Graph object and the signals that connect them are highlighted yellow in the block diagram. Highlighting the blocks also shades the canvas a darker gray to make the highlighting more visible.
highlight(x2Sources)
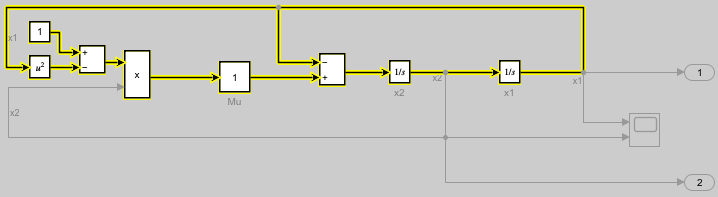
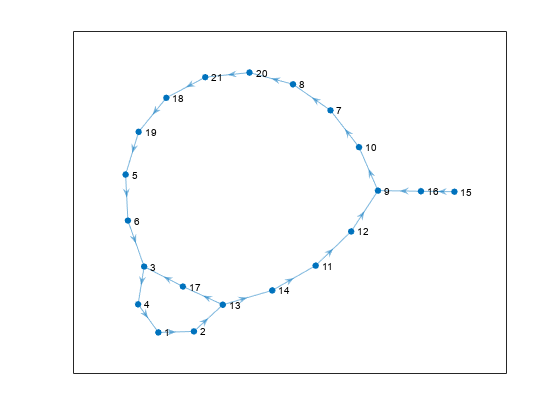
The sltrace.Graph object includes a digraph object you can use to analyze the connections among the source blocks. Each node in the graph represents a block port, and each edge, or line, represents a signal line.
plot(x2Sources.TraceGraph)
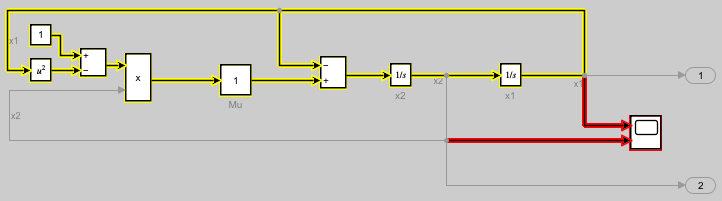
Once you have an sltrace.Graph object, you can use the highlight function to highlight any block or signal line in the model, including blocks and signal lines that are not part of the signal trace information in the sltrace.Graph object. For example, highlight the Scope block and the signal lines connected to the input ports on the Scope block.
Use the get_param function to get the block handle for the Scope block.
scopePath = mdl + "/Scope"; scopeHandle = get_param(scopePath,"Handle");
Use the get_param function to get the port handles for the Scope block.
scopePorts = get_param(scopePath,"PortHandles");Use the get_param function to get the line handle for the signal line connected to each input port of the Scope block.
scopeIn1 = scopePorts.Inport(1); scopeIn1 = get_param(scopeIn1,"Line"); scopeIn2 = scopePorts.Inport(2); scopeIn2 = get_param(scopeIn2,"Line");
Use the highlight function to highlight the elements in the block diagram. The Scope block and the input signals for the Scope block are highlighted red in the block diagram, which still shows the yellow highlighting on the sources for the signal x2.
highlight(x2Sources,[scopeHandle scopeIn1 scopeIn2])
To remove the highlighting, use the removeHighlight function. The function removes all highlighting in the block diagram associated with the sltrace.Graph object. When the block diagram contains no highlighting, the shading in the canvas is also removed.
removeHighlight(x2Sources)
Input Arguments
Port from which to trace, specified as a port handle.
When the specified port is a block input port, the function traces the signal to the first nonvirtual source block.
When the specified port is a block output port, the function traces the signal to the first nonvirtual destination block.
Block from which to trace, specified as a block handle, a Simulink.BlockPath object, or a string or a character vector that defines
the path to a block.
Tracing direction, specified as 'Source' or
'Destination'.
'Source'— Trace signals on block input ports to sources.'Destination'— Trace signals on block output ports to destinations.
When you want to trace the sources or destinations for only one input or output
port, use the Port name-value argument to specify the signal to
trace.
When you want to trace the sources or destinations for a specific element within a
bus, use the Element name-value argument to specify the element to
trace.
Data Types: char | string
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: sltrace(prt,TraceAll="on",BlockPath="on")
Option to trace to all sources or destinations, specified as
'off' or 'on'.
'off'— Trace the signal to the first nonvirtual source or destination block.'on'— Trace the signal to all source or destination blocks.
Example: sltrace(blk,"Source",TraceAll="on") traces all sources
for input signals of the block blk.
Data Types: char | string
Endpoint for tracing, specified as a block handle, a Simulink.BlockPath object, or a string or character vector that defines
the path to a block.
If the specified block is not on the tracing path for the signal, the function traces the signal to all source or destination blocks.
Example: sltrace(blk,"Destination",Stop="mdl/blk") traces the
output signals of block blk to all destination blocks up to the
block blk in the model mdl.
Index of port from which to trace, specified as a real positive scalar number.
Use this argument when you specify the signal path to trace as a block and direction and the block has multiple input or output ports.
When you trace signal sources, specify the index of the input port to which the signal you want to trace connects.
When you trace signal destinations, specify the index of the output port that produces the signal you want to trace.
When you do not specify this name-value argument, the function traces the signals on all input or output ports.
Example: sltrace("mdl/blk","Source",Port="2") traces all sources
for the signal on output port 2 of the block blk
in the model mdl.
Data Types: double | single
Bus element from which to trace, specified as a string or a character vector that defines the name of the bus element.
Use this argument when you specify the signal path to trace as a block and direction and the block receives or produces a bus. When you do not specify this name-value argument, the function traces all bus elements.
Example: sltrace("mdl/blk","Destination",Element="b") traces the
element b of the bus produced by the block blk
in model mdl to the first nonvirtual destination
block.
Data Types: char | string
Option to capture block information using Simulink.BlockPath
objects, specified as 'off' or 'on'. The
sltrace.Graph object includes information about the source or
destination blocks in the specified tracing path. This argument specifies how the
block information is provided in the sltrace.Graph object.
'off'— Thesltrace.Graphobject contains the block handle for each source or destination block.'on'— Thesltrace.Graphobject contains aSimulink.BlockPathobject for each source or destination block.
Specify this name-value argument as 'on' when the model
contains multiple instances of a referenced model.
Example: sltrace("mdl/blk","Source",BlockPath="on") traces all
sources for input signals of the block blk in the model
mdl and captures the block information using
Simulink.BlockPath objects.
Output Arguments
Signal sources or destinations, returned as an sltrace.Graph object. The object includes information about blocks in the
tracing path and a digraph object you can use to plot a directed graph
of the path. You can use the highlight function to highlight the
tracing path in the block diagram.
Version History
Introduced in R2021bTo better support scripting workflows, the sltrace
function now loads models instead of opening them. The highlight and
removeHighlight functions still open the model to show the highlighted signal
trace in the model.
See Also
Objects
Functions
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleccione un país/idioma
Seleccione un país/idioma para obtener contenido traducido, si está disponible, y ver eventos y ofertas de productos y servicios locales. Según su ubicación geográfica, recomendamos que seleccione: .
También puede seleccionar uno de estos países/idiomas:
Cómo obtener el mejor rendimiento
Seleccione China (en idioma chino o inglés) para obtener el mejor rendimiento. Los sitios web de otros países no están optimizados para ser accedidos desde su ubicación geográfica.
América
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)