Variant Start
Libraries:
Simulink /
Signal Routing
Description
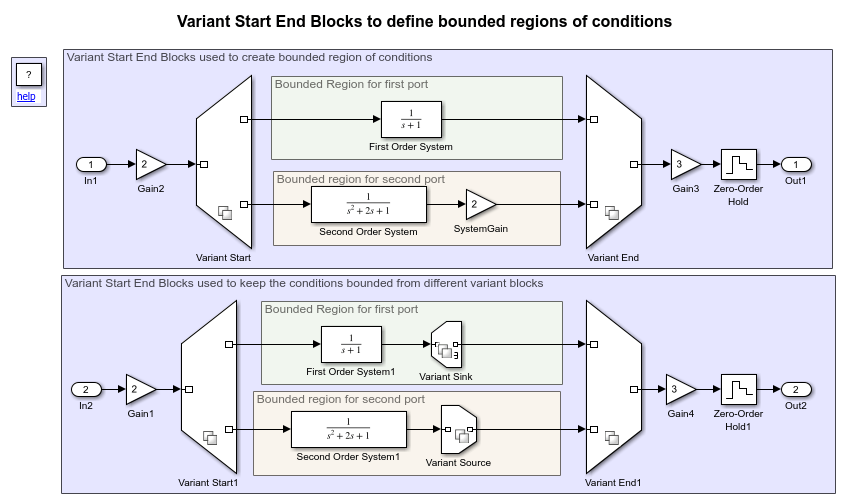
The Variant Start block defines the start of the bounded region that allows you to limit variant condition propagation without introducing a level of hierarchy. Define the end of the bounded region by using Variant End. For every Variant Start block, there is a single corresponding Variant End block. When you specify the variant conditions on the Variant Start block, the corresponding Variant End block inherits the conditions and other parameters based on the unique Variant Start End Tag on compile.
In a given hierarchy, a region between the outport of a Variant Start block and the corresponding inport of the Variant End block is defined as a bounded region if the following conditions are met:
You can create a subsystem that wraps all the blocks within the choice without intersecting with the other choice. Thus, there is a clear demarcation of choices.
You can create a subsystem with only one inport(connected to the outport of the Variant Start block), and only one outport (connected to the outport of the destination). Choices do not branch out of the region.
Examples
Control Variant Condition Propagation using Variant Start and Variant End Blocks
Confine variations to a set of blocks and control their activation collectively using Variant Start and Variant End blocks.
Generate Code for Variant Start and Variant End Blocks
Generate code for specific implementation of component represented using Variant Start and Variant End blocks.
(Simulink Coder)
Limitations
The Variant Start block works with time-based, and action signals. You cannot use SimEvents®, Simscape™ Multibody™, or other non-time-based signals with these blocks.
Including these blocks within the bounded region formed by the Variant Start and Variant End blocks is not supported, as variant conditions could extend beyond the bounded region when their corresponding pair blocks are located outside of it.
Entity Multicast (SimEvents) and Queue (SimEvents)
Merging signals from variant choices of a Variant Start block into a bus is not supported; however, they can be routed to separate buses.
Ports
Input
Input signal to be connected to the active output port.
Data Types: single | double | half | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point | enumerated | bus | struct
Output
Output branch that forms the start of the bounded region with corresponding inport of the Variant End block.
Data Types: single | double | half | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point | enumerated | bus
Output signal from the Nth branch.
Data Types: single | double | half | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point | enumerated | bus
Parameters
Unique identifier to identify the correct Variant Start and
Variant End pair that form the bounded region, specified as a valid
MATLAB identifier. A valid MATLAB identifier is a character vector of alphanumerics (A–Z, a–z, 0–9) and
underscores, such that the first character is a letter and the length of the character
vector is less than or equal to namelengthmax.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
VariantStartEndTag
|
| Type: character vector |
Values:
'A' | valid MATLAB identifier |
Default:
'A'
|
The variant control that determines the active variant choice can be any of these types.
expression— The software chooses the active variant based on the evaluation of the variant conditions. When a condition expression evaluates totrue, the corresponding variant choice becomes active. When a condition expression evaluates tofalse, the corresponding variant choice becomes inactive. See Switch Between Choices Using Condition Expressions in Variant Blocks.label— The software chooses the active variant based on the name of the variant. The variant control is a string and does not require you to create any variable in any workspaces. See Switch Between Choices Using Labels in Variant Blocks.sim codegen switching— Automatically switch between the variants for simulation and code generation workflows without creating any workspace variable. When you simulate a model, the software automatically chooses thesimbranch as the active choice. Similarly, when you do a software-in-the-loop (SIL) or processor-In-Loop (PIL) simulation, generate code, or use external mode, the software automatically chooses thecodegenbranch. See Switch Between Choices for Simulation and Code Generation Workflows Without Using Control Variables in Variant Blocks.
For more information on variant control modes, see Introduction to Variant Controls. For a comparison between different types of variant control modes, see Compare Different Types of Variant Control Modes in Variant Blocks.
Dependencies
The availability of different variant activation times depends on the type of the Variant control mode that you specify. The Variant activation time parameter determines the time when the software sets the active choice. The parameter also determines which variability to include in the generated code. This table explains the variant activation time supported by each variant control mode.
| Variant activation time | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant control mode | update diagram | update diagram analyze all
choices | code compile | startup |
expression | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
label | ✓ | x | x | x |
sim codegen switching | ✓ | ✓ | x | x |
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
VariantControlMode
|
| Type: character vector |
Values:
'expression' | 'label' | 'sim
codegen switching' |
Default:
'expression'
|
This parameter determines which variability to include in the simulation and code generation workflows. For more information, see Activate Variant During Different Stages of Simulation and Code Generation Workflow.
update diagram— When you execute the model, only the active choice is included in the simulation and the code generation workflow. Generated code contains only the active choice.update diagram analyze all choices— When you execute the model, both active and inactive choices are analyzed for consistency across the model. However, only the active choice is included in the simulation and the code generation workflow. Generated code contains only the active choice.code compile— When you execute the model, both active and inactive choices are analyzed for consistency across the model, and all choices are included in the simulation and the code generation workflow. Generated code contains both the active and inactive choices enclosed in the preprocessor conditionals#ifand#elif. However, the executable built from the generated code contains only active choice.startup— When you execute the model, both active and inactive choices are analyzed for consistency across the model, and all choices are included in the simulation and the code generation workflow. With this option, you can improve the speed of iterative simulations using fast restart. For more information, see Run Iterative Simulations Without Recompiling Model for Variant Systems Using Fast Restart. Code generated from the model contains both the active and inactive choices that are enclosed in regularifconditions. The executable built from the generated code also contains both active and inactive choices.inherit from Simulink.VariantControl— When you execute the model, the block inherits the activation time from its variant control variables of typeSimulink.VariantControl. If a variant block has multiple variant control variables of typeSimulink.VariantControl, then all those variables must have the same activation time.
Dependencies
The availability of different variant activation times depends on the type of the variant control mode that you specify. The Variant activation time parameter determines when the software sets the active choice. The parameter also determines which variability to include in the generated code. This table explains the variant activation time supported by each variant control mode.
| Variant activation time | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant control mode | update diagram | update diagram analyze all
choices | code compile | startup |
expression | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
label | ✓ | x | x | x |
sim codegen switching | ✓ | ✓ | x | x |
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
VariantActivationTime
|
| Type: character vector |
Values:
'update diagram' | 'update diagram analyze all
choices' | 'code compile' |
'startup'
|
Default:
'update diagram'
|
The table has a row for each variant choice connected to the output port of the Variant Start block. If there are no variant choices, the table is empty.
You can use buttons to the left of the Port and associated conditions table to modify the elements in the table.
| To... | Click... |
|---|---|
Add a new output port: Create a new output port as a variant choice and add an entry for the new choice in the table. | |
Delete selected port: Delete the selected variant choice from the block and its entry from the table. | |
Create/Edit selected variant object: Create or
edit a Note For a model that uses the base workspace, this operation creates the
|
This parameter is read-only.
Number of the output port that is connected to one variant choice upstream of the Variant Start block. This value is read-only.
Click ![]() to add a port or
to add a port or ![]() to delete an existing one.
to delete an existing one.
A name for a choice, specified as a string.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Variant control mode to
label.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use
the set_param function.
To get the block parameter value
programmatically, use the get_param function.
| Parameter: | VariantControl |
| Values: | variant control that is associated with the variant choice |
| Data Types: | char |
Example: set_param(gcb, 'VariantControl', 'V == 3'), where
gcb is the variant choice of the Variant Start
block.
Example: get_param(gcb, 'VariantControl'), where
gcb is the variant choice of the Variant Start
block.
Specify the condition expression to determine the active choice. When a condition
expression evaluates to true, the software activates the
corresponding variant choice. When a condition expression evaluates to
false, the software deactivates the corresponding variant
choice.
The variant controls can be:
Boolean condition expression for rapid prototyping. For example,
A == 1,A ~= B,A && B == 1, and so on.A
Simulink.VariantExpressionobject that contains a condition expression for condition reuse. See Simulink.VariantExpression Objects for Variant Condition Reuse of Variant Blocks.Default Variant Choice if none of the choices evaluates to
true.
Here, A and B are operands called
as variant control variables. ==,
~=, and && are operators in the
condition expression. The condition expression can contain one or more such variant
control variables and operators. For information on supported types and storage location
of variant control variables, see Types of Variant Control Variables (Operands) in Variant Blocks and Storage Locations for Variant Control Variables (Operands) in Variant Blocks. For information
on operators, see Types of Operators in Variant Blocks for Different Activation Times.
For more information, see Switch Between Choices Using Condition Expressions in Variant Blocks.
In Variant Assembly Subsystem block, this parameter is a list of
auto-generated boolean expressions with Variant control variable on
the left-hand side and the members of the Variant enumeration
choice are on the right-hand side of the expressions. Both the sides of
the expressions are connected with ==. This parameter is
read-only.
Programmatic Use
To set the block parameter value programmatically, use
the set_param function.
To get the block parameter value
programmatically, use the get_param function.
Variant Subsystem block:
| Parameter: | VariantControl |
| Values: | variant control that is associated with the variant choice |
| Data Types: | char |
Example: set_param(gcb, 'VariantControl', 'V == 3'), where
gcb is the variant choice of the Variant
Subsystem block.
Example: get_param(gcb, 'VariantControl'), where
gcb is the variant choice of the Variant
Subsystem block.
Variant Source and Variant Sink blocks:
| Parameter: | VariantControls |
| Values: | variant controls that are associated with variant choices |
| Data Types: | char |
Example: set_param(gcb, 'VariantControls', {'A == 1','A ==
2'}), where gcb is the Variant
Sink or Variant Source block.
Example: get_param(gcb, 'VariantControls'), where
gcb is the Variant Sink or Variant
Source block.
This parameter is read-only.
This parameter displays the condition expression specified as
Simulink.VariantExpression object. To change or edit the condition
expression, use the Simulink.VariantExpression parameter dialog box
that appears when you double-click the object in the workspace.
Note
The operands that you specify in a condition expression of type
Simulink.VariantExpression must be defined in the base
workspace or a data dictionary. Specifying operands that are defined in the mask
or model workspace is not supported.
This list contains the labels of all the variant choices. To set an active choice, select a label from the list. The corresponding choice becomes active. Alternatively, to change the active choice in label mode, you can follow the approaches described in Set Active Choices Using Variant Control Labels.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Variant control mode to
label.
Programmatic Use
Parameter:
LabelModeActiveChoice
|
| Type: character vector |
| Value: If no label mode active choice is specified, the value is empty. If a label mode active choice is specified, the value is the variant control label for the active choice. |
Default: '' |
When you select this option, Simulink® annotates the variant condition expression on each port of the Variant Start block.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
ShowConditionOnBlock
|
| Type: character vector |
Values:
'off' | 'on'
|
Default:
'off'
|
Block Characteristics
Data Types |
|
Direct Feedthrough |
|
Multidimensional Signals |
|
Variable-Size Signals |
|
Zero-Crossing Detection |
|
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using Simulink® Coder™.
Fixed-Point Conversion
Design and simulate fixed-point systems using Fixed-Point Designer™.
Version History
Introduced in R2024a
See Also
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleccione un país/idioma
Seleccione un país/idioma para obtener contenido traducido, si está disponible, y ver eventos y ofertas de productos y servicios locales. Según su ubicación geográfica, recomendamos que seleccione: .
También puede seleccionar uno de estos países/idiomas:
Cómo obtener el mejor rendimiento
Seleccione China (en idioma chino o inglés) para obtener el mejor rendimiento. Los sitios web de otros países no están optimizados para ser accedidos desde su ubicación geográfica.
América
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)