Connect Blocks Programmatically
To connect blocks with signal lines programmatically, the model, library, or subsystem
containing the blocks must be loaded. For information about how to load models, libraries, and
subsystems, see Create, Load, Open, Save, and Close Models Programmatically. To make a connection,
use the Simulink.connectBlocks function. This syntax connects the source specified by
src to the destination specified by dst.
connection = Simulink.connectBlocks(src,dst)
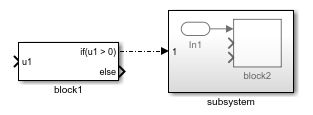
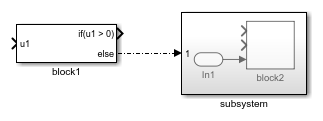
For example, suppose you have a model named myModel that contains a
block named block1 and a subsystem named subsystem. The
subsystem contains a block named block2. These commands connect the block
named block1 to the block named block2 at any available
ports.
src = "myModel/block1"; dst = "myModel/subsystem/block2"; connection = Simulink.connectBlocks(src,dst)
By default, the Simulink.connectBlocks function uses smart automatic
line routing. Smart automatic line routing creates signal lines composed of orthogonal line
segments that avoid overlapping other blocks and signal lines. If line routing is causing a
significant increase in run time, consider turning off smart automatic line routing. Turning
off smart automatic line routing reduces runtime, but connects blocks on the most direct route
without avoiding overlap or forcing the signal lines to be orthogonal. To turn off smart
automatic line routing, use this syntax.
connection = Simulink.connectBlocks(src,dst,...
RoutingStyle=Simulink.Connection.RoutingStyle.Direct)Connecting blocks using the Simulink.connectBlocks function creates
signal lines and blocks. For example, connecting a block at the root level of the model to a
block in a subsystem creates signal lines and an Inport block in the subsystem.
You can get the type, handles, and paths of the new signal lines and blocks from the function
output.
Specify Connection Source and Destination
To programmatically connect blocks using the Simulink.connectBlocks
function, specify the source and destination of the connection as the first two input
arguments. The source and destination can be on different levels of the model hierarchy.
To connect both blocks at any available port, specify both the source and destination as block handles, or specify both as block paths. To connect both blocks at a specific port, specify both the source and destination as port handles, or specify both as port paths. Connecting one block at a specific port and the other at any available port is not supported. For information about how to get handles and paths, see Get Handles and Paths.
The destination must be an unconnected port or a block that has at least one unconnected port. The source can be fully connected. If the source is fully connected, the signal line branches to make the connection.
The table shows examples of how to specify the source and destination of a connection.
| Action | Example |
|---|---|
| Connect two blocks at any available ports. | A model named src = getSimulinkBlockHandle("myModel/block1"); dst = getSimulinkBlockHandle("myModel/mySubsystem/block2"); connection = Simulink.connectBlocks(src,dst)
|
| Connect two blocks at specific ports. | A model named Use the allPortsBlock1 = get_param("myModel/block1","PortHandles"); src = allPortsBlock1.Outport(2); Use the same approach to get the handle of the bottom input port of the block named
allPortsBlock2 = get_param("myModel/subsystem/block2","PortHandles"); dst = allPortsBlock2.Inport(3); connection = Simulink.connectBlocks(src,dst)
|
Connect any port on a multi-port block to a block that has only one compatible port available for connection. | A model named Since you do not need to specify which ports to connect to one either block, you can specify the source and destination as block handles or block paths. src = getSimulinkBlockHandle("myModel/block1"); dst = getSimulinkBlockHandle("myModel/block2"); connection = Simulink.connectBlocks(src,dst)
|
Connect a specific port on a multi-port block to a block that has only one compatible port available for connection. | A model named To connect to a specific port on one block, you must specify both the source and destination as specific port handles or port paths. allPortsBlock1 = get_param("myModel/block1","PortHandles"); src = allPortsBlock1.Outport(2); allPortsBlock2 = get_param("myModel/subsystem/block2","PortHandles"); dst = allPortsBlock2.Inport; connection = Simulink.connectBlocks(src,dst)
|
| Connect a block with only one output port to a block with only one unconnected input port. | A model named Since you do not need to specify which ports to connect to one either block, you can specify the source and destination as blocks handles or block paths. src = getSimulinkBlockHandle("myModel/block1"); dst = getSimulinkBlockHandle("myModel/block2"); connection = Simulink.connectBlocks(src,dst)
|
| Branch a signal line. | A model named Since the source is already connected, the signal line branches to make the new connection. src = getSimulinkBlockHandle("myModel/block1"); dst = getSimulinkBlockHandle("myModel/block3"); connection = Simulink.connectBlocks(src,dst)
|
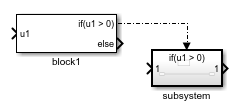
| Connect a block to the control input port on a conditionally executed subsystem. | A model named allPortsMyBlock2 = get_param("myModel/myBlock2","PortHandles"); src = portsMyBlock2.Outport; allPortsMySubsystem = get_param("myModel/mySubsystem","PortHandles"); dst = portsMySubsystem.Ifaction; connection = Simulink.connectBlocks(src,dst) The third command gets the handles of all ports on the If Action Subsystem block and stores the handles in a vector. The last command extracts the handle of the control input port from the vector using dot notation and the port name. To get the port names of the control input ports of other conditionally executed subsystems, see Get Port Name.
|
Get Types, Handles, and Paths of Model Elements Created by Simulink.connectBlocks Function
In this syntax, connection is an object that stores the types,
handles, and paths of the model elements the Simulink.connectBlocks
function creates to make the connection. The model elements can be signal lines or blocks.
Paths are only output for blocks.
connection = Simulink.connectBlocks(src,dst)
The table shows how you can extract the types, handles, and paths of the signal lines
and blocks from the object. The commands in the table assume the object is stored in a
variable named connection. For more information about these commands, see
Get Types, Handles, and Paths of Model Elements Created by Simulink.connectBlocks Function.
| Action | Command | Example Output |
|---|---|---|
| Get the handles of all signal lines created. |
transits = connection.getTransits;
isLine = arrayfun(@(x)x.getType=="line",transits);
lineTransits = transits(isLine);
h = arrayfun(@(x)x.getHandle,lineTransits)
|
h = 357.0001 358.0002 |
| Get the handles of all blocks created. |
transits = connection.getTransits;
isBlock = arrayfun(@(x)x.getType=="block",transits);
blockTransits = transits(isBlock);
h = arrayfun(@(x)x.getHandle,blockTransits)
|
h = 354.0002 |
| Get the paths of all blocks created. |
transits = connection.getTransits;
isBlock = arrayfun(@(x)x.getType=="block",transits);
blockTransits = transits(isBlock);
paths = arrayfun(@(x)x.getName,blockTransits,UniformOutput=false)
|
paths =
1×1 cell array
{'myModel/mySubsystem/myBlock'} |
Delete Signal Lines
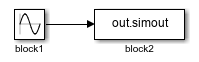
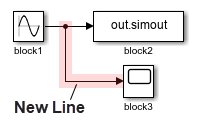
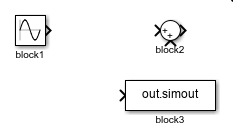
To delete signal lines, use the delete_line function. For example, suppose you have a model named
myModel containing a Sine Wave block named
block1 that connects to a Sum block named
block2 and to a From Workspace block named
block3. The table shows how to delete signal lines and branches of
signal lines in the model. For more syntaxes, see the delete_line
function documentation. To delete multiple signal lines or branches at once, specify the
function input as a vector of line handles.
| Action | Example |
|---|---|
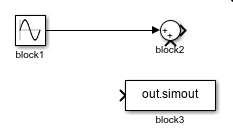
| Delete a signal line, including all branches. | Delete the signal line that connects to the block named
To delete a
signal line with all branches, identify the block to whose output port the signal
line connects, which in this example is the block named allLinesBlock1 = get_param("myModel/block1","LineHandles") Extract the handle of the signal line you want to delete using dot notation and the name of the port to which the signal line connects. For more information, see Specify Signal and Signal Line. hOutport = allLinesBlock1.Outport; Delete the signal line. delete_line(hOutport)
|
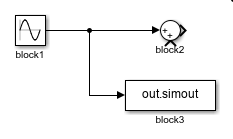
| Delete one branch of a signal line. | Delete the branch of the signal line that connects to the block named
To delete a branch of a signal line,
identify the block to whose input port the branch connects, which in this example
is the block named allLinesBlock3 = get_param("myModel/block3","LineHandles") Extract the handle of the branch you want to delete using dot notation and the name of the port to which the branch connects. For more information, see Specify Signal and Signal Line. hInput = allLinesBlock3.Inport; Delete the branch. delete_line(hInput)
|
Delete Connection Made Using Simulink.connectBlocks Function
If you connect blocks in an open model, you can interactively undo the connection by pressing Ctrl+z. When the model is closed, the interactive undo is not supported.
You can programmatically undo a connection made using the
Simulink.connectBlocks function by deleting all the signal lines and
blocks created to make the connection, provided you did not delete or modify the handles of
any of these model elements after making the connection.
Suppose you stored the output of the
Simulink.connectBlocksfunction in a variable namedconnection.connection = Simulink.connectBlocks(src,dst)
Use these commands get the handles of all signal lines created to make the connection. For more information about the commands, see Get Types, Handles, and Paths of Model Elements Created by Simulink.connectBlocks Function.
transits = connection.getTransits; isLine = arrayfun(@(x)x.getType=="line",transits); lineTransits = transits(isLine); hLines = arrayfun(@(x)x.getHandle,lineTransits) isBlock = arrayfun(@(x)x.getType()=="block",transits); blockTransits = transits(isBlock); hBlocks = arrayfun(@(x)x.getHandle,blockTransits)
Use the
delete_linefunction to delete all the signal lines created to make the connection.delete_line(hLines)
Use the
delete_blockfunction to delete all the blocks created to make the connection.delete_block(hBlocks)
Comment Out and Comment Through Blocks
You can exclude blocks from simulation without physically removing the blocks from the model by commenting out or commenting through the blocks.
Comment out — Excludes the selected block from simulation. The signals are terminated and grounded.
Comment through — Excludes the selected block from simulation. The signals are passed through. To comment through, a block must have the same number of input and output ports and no control or connection ports.
Note
These Simulink® blocks do not support being commented out or commented through:
Inport
Outport
Connection Port
Argument Inport
Argument Outport
Data Store Memory
Goto Tag Visibility
The Signal Generator block does not support being commented through.
To view or change the commented state of a block programmatically, use the get_param and set_param functions. The table shows the
commands you can use to take these actions on a block with the handle h.
For information about how to get block handles, see Get Handles and Paths.
| Action | Command |
|---|---|
| View whether a block is commented out or through. |
get_param(h,"commented") |
| Comment out a block. |
set_param(h,commented="on") |
| Comment through a block. |
set_param(h,commented="through") |
| Uncomment a block. |
set_param(h,commented="off") |
See Also
Simulink.connectBlocks | delete_line | delete_block | get_param | set_param