driving.scenario.roadBoundariesToEgo
Convert road boundaries to ego vehicle coordinates
Syntax
Description
egoRoadBoundaries = driving.scenario.roadBoundariesToEgo(scenarioRoadBoundaries,ego)ego.
egoRoadBoundaries = driving.scenario.roadBoundariesToEgo(scenarioRoadBoundaries,egoPose)egoPose.
Examples
Create a driving scenario containing a figure-8 road specified in the world coordinates of the scenario. Convert the world coordinates of the scenario to the coordinate system of the ego vehicle.
Create an empty driving scenario.
scenario = drivingScenario;
Add a figure-8 road to the scenario. Display the scenario.
roadCenters = [0 0 1
20 -20 1
20 20 1
-20 -20 1
-20 20 1
0 0 1];
roadWidth = 3;
bankAngle = [0 15 15 -15 -15 0];
road(scenario,roadCenters,roadWidth,bankAngle);
plot(scenario)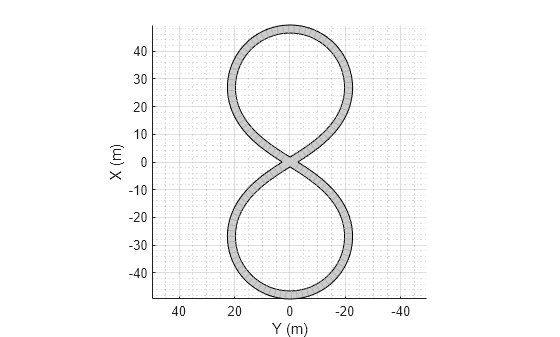
Add an ego vehicle to the scenario. Position the vehicle at world coordinates (20, –20) and orient it at a –15 degree yaw angle.
ego = actor(scenario,'ClassID',1,'Position',[20 -20 0],'Yaw',-15);
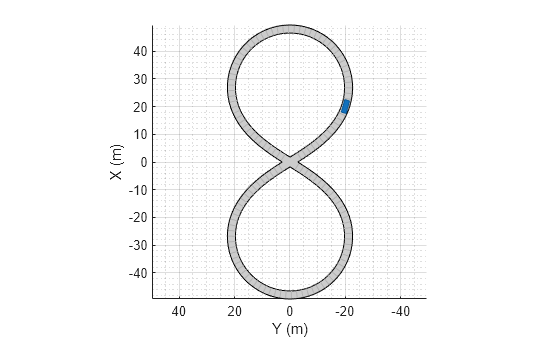
Obtain the road boundaries in ego vehicle coordinates by using the roadBoundaries function. Specify the ego vehicle as the input argument.
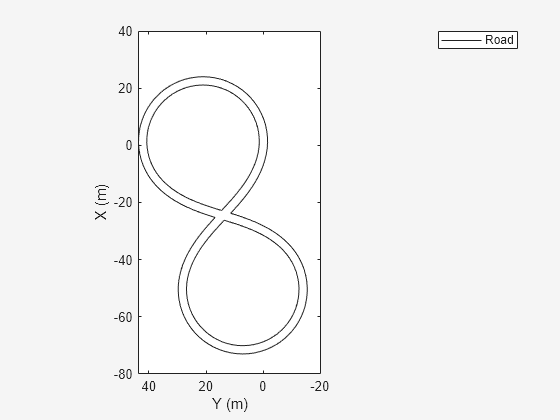
rbEgo1 = roadBoundaries(ego);
Display the result on a bird's-eye plot.
bep = birdsEyePlot; lbp = laneBoundaryPlotter(bep,'DisplayName','Road'); plotLaneBoundary(lbp,rbEgo1)
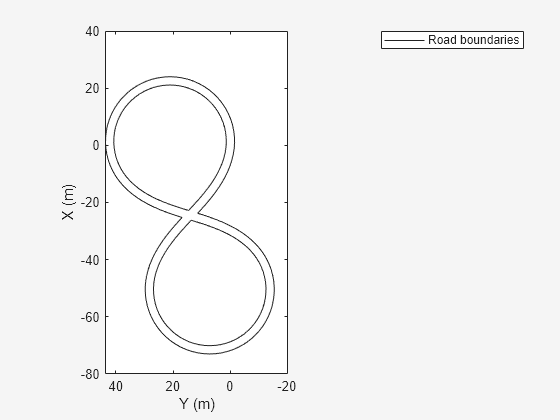
Obtain the road boundaries in world coordinates by using the roadBoundaries function. Specify the scenario as the input argument.
rbScenario = roadBoundaries(scenario);
Obtain the road boundaries in ego vehicle coordinates by using the driving.scenario.roadBoundariesToEgo function.
rbEgo2 = driving.scenario.roadBoundariesToEgo(rbScenario,ego);
Display the road boundaries in ego vehicle coordinates on a bird's-eye plot.
bep = birdsEyePlot; lbp = laneBoundaryPlotter(bep,'DisplayName','Road boundaries'); plotLaneBoundary(lbp,{rbEgo2})
Input Arguments
Road boundaries of the scenario in world coordinates, specified as a 1-by-N cell array. N is the number of road boundaries within the scenario. Each cell corresponds to a road and contains the (x, y, z) coordinates of the road boundaries in a real-valued P-by-3 matrix. P is the number of boundaries and varies from cell to cell. Units are in meters.
Ego actor pose in the world coordinates of a driving scenario, specified as a structure.
The ego actor pose structure must contain at least these fields.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
ActorID | Scenario-defined actor identifier, specified as a positive integer. |
In R2024b:
| Front-axle position of the vehicle, specified as a three-element row vector in the form [x y z]. Units are in meters. Note If the driving scenario does not contain a
front-axle trajectory for at least one vehicle,
then the
|
Position | Position of actor, specified as a real-valued vector of the form [x y z]. Units are in meters. |
Velocity | Velocity (v) of actor in the x- y-, and z-directions, specified as a real-valued vector of the form [vx vy vz]. Units are in meters per second. |
Roll | Roll angle of actor, specified as a real-valued scalar. Units are in degrees. |
Pitch | Pitch angle of actor, specified as a real-valued scalar. Units are in degrees. |
Yaw | Yaw angle of actor, specified as a real-valued scalar. Units are in degrees. |
AngularVelocity | Angular velocity (ω) of actor in the x-, y-, and z-directions, specified as a real-valued vector of the form [ωx ωy ωz]. Units are in degrees per second. |
For full definitions of these structure fields, see the actor and vehicle functions.
Output Arguments
Road boundaries in ego vehicle coordinates, returned as a real-valued Q-by-3 matrix. Q is the number of road boundary point coordinates of the form (x, y, z).
All road boundaries are contained in the same matrix, with a row of
NaN values separating points in different road
boundaries. For example, if the input has three road boundaries of length
P1,
P2, and
P3, then Q
= P1 +
P2 +
P3 + 2. Units are in
meters.
Version History
Introduced in R2017a
See Also
Objects
Functions
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleccione un país/idioma
Seleccione un país/idioma para obtener contenido traducido, si está disponible, y ver eventos y ofertas de productos y servicios locales. Según su ubicación geográfica, recomendamos que seleccione: .
También puede seleccionar uno de estos países/idiomas:
Cómo obtener el mejor rendimiento
Seleccione China (en idioma chino o inglés) para obtener el mejor rendimiento. Los sitios web de otros países no están optimizados para ser accedidos desde su ubicación geográfica.
América
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)