fxpOptimizationOptions Class
Specify options for data type optimization
Description
The fxpOptimizationOptions object enables you to specify options and
constraints to use during the data type optimization process using fxpopt.
Creation
options = fxpOptimizationOptions()fxpOptimizationOptions object with default values.
options = fxpOptimizationOptions('PropertyName',PropertyValue) fxpOptimizationOptions object with specified property name-value
pairs.
Properties
Maximum number of iterations to perform, specified as a nonnegative scalar integer. The optimization process iterates through different solutions until it finds an ideal solution, reaches the maximum number of iterations, or reaches another stopping criteria.
Example: options.MaxIterations = 75;
Example: options =
fxpOptimizationOptions('MaxIterations',75);
Data Types: double
Maximum amount of time for the optimization to run, in seconds, specified as a nonnegative scalar. The optimization runs until it reaches the time specified, finds an ideal solution, or reaches another stopping criteria.
Example: options.MaxTime = 1000;
Example: options =
fxpOptimizationOptions('MaxTime',1000);
Data Types: double
Maximum number of iterations where no new best solution is found, specified as a scalar integer. The optimization continues as long as the algorithm continues to find new best solutions.
Example: options.Patience = 15;
Example: options =
fxpOptimizationOptions('Patience',15);
Data Types: double
The level of information displayed at the command line during the optimization process, specified as one of these values:
'High'— Information is displayed at the command line at each iteration of the optimization process, including whether a new best solution was found and the cost of the solution.'Moderate'— Information is displayed at each major step of the optimization process, including when the process is in the preprocessing, modeling, and optimization phases.'Silent'— Nothing is displayed at the command line until the optimization process is finished.
Example: options.Verbosity = 'Moderate';
Example: options =
fxpOptimizationOptions('Verbosity','Moderate');
Data Types: char | string
Specify the word lengths that can be used in your optimized system under design. Use
this property to target the neighborhood search of the optimization process. The final
result of the optimization uses word lengths in the intersection of the
AllowableWordLengths and word lengths compatible with hardware
constraints specified in the Hardware Implementation pane of your
model.
Example: options.AllowableWordLengths =
[8:11,16,32];
Data Types: double
Objective function to use during optimization search, specified as one of these values:
'BitWidthSum'— Minimize total bit width sum.'OperatorCount'— Minimize estimated count of operators in generated C code.This option may result in a lower program memory size for C code generated from Simulink® models. The
'OperatorCount'objective function is not suitable for FPGA or ASIC targets.Note
To use
'OperatorCount'as the objective function during optimization, the model must be ready for code generation. For more information about determining code generation readiness, see Check Model and Configuration for Code Generation (Embedded Coder).'CustomCostFunction'— Customize the objective function by specifying cost functions for blocks in your design.
Example: options.ObjectiveFunction =
'OperatorCount';
Data Types: char | string
Whether to run iterations of the optimization in parallel, specified as a logical
0 (false) or 1 (true). Running the iterations in
parallel requires a Parallel Computing Toolbox™ license. If you do not have a Parallel Computing Toolbox license, or if you specify 0 (false), the iterations
run in serial.
Example: options.UseParallel = 1;
Data Types: logical
Additional advanced options for optimization.
AdvancedFxpOptimizationOptions is an object containing additional
properties that can affect the optimization.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
PerformNeighborhoodSearch |
|
EnforceLooseCoupling | Some Simulink blocks have a parameter that forces inputs to share a data type, or forces the output to share the same data type as the input.
|
UseDerivedRangeAnalysis |
Depending on the model configuration, derived range analysis may take longer than simulation of the model. |
SimulationScenarios | Define additional simulation scenarios to consider during optimization
using a Simulink.SimulationInput object.
For an example, see Optimize Data Types Using Multiple Simulation Scenarios. |
SafetyMargin | Enter a safety margin, specified as a nonnegative scalar value indicating the percentage increase in the bounds of the collected range. The safety margin is applied to the union of all collected ranges, including simulation ranges, derived ranges, and design ranges. |
DataTypeOverride | Override data types specified in the model when simulating during the range collection phase of optimization.
|
HandleUnsupported | Some blocks are not supported for fixed-point conversion. Specify how the optimizer handles unsupported blocks.
For more information, see Blocks That Do Not Support Fixed-Point Data Types. |
PerformSlopeBiasCancellation |
|
InstrumentationContext | [model '/Subsystem'] — Restrict instrumentation for
minimum, maximum, and overflow logging for the range collection step of
optimization to a subsystem. The subsystem must be under the top-level model
and contain the system under design. |
Example: options.AdvancedOptions.PerformNeighborhoodSearch =
0;
Methods
addSpecification | Specify known data types in a system |
addTolerance | Specify numeric tolerance for optimized system |
showSpecifications | Show specifications for a system |
showTolerances | Show tolerances specified for a system |
setCustomCost | Set block-level cost functions to customize the optimization objective |
Examples
Create an fxpOptimizationObject with default property values.
options = fxpOptimizationOptions();
Edit the properties after creation using dot syntax.
options.Patience = 15; options.AllowableWordLengths = [8,16,32]; options.AdvancedOptions.UseDerivedRangeAnalysis = true
options =
fxpOptimizationOptions with properties:
MaxIterations: 50
MaxTime: 600
Patience: 15
Verbosity: High
AllowableWordLengths: [8 16 32]
ObjectiveFunction: BitWidthSum
UseParallel: 0
Advanced Options
AdvancedOptions: [1×1 DataTypeOptimization.AdvancedFxpOptimizationOptions]
Use property name-value pairs to set properties at object creation.
options = fxpOptimizationOptions('Patience',15,'AllowableWordLengths',[8,16,32])
options =
fxpOptimizationOptions with properties:
MaxIterations: 50
MaxTime: 600
Patience: 15
Verbosity: High
AllowableWordLengths: [8 16 32]
ObjectiveFunction: BitWidthSum
UseParallel: 0
Advanced Options
AdvancedOptions: [1×1 DataTypeOptimization.AdvancedFxpOptimizationOptions]
Specify advanced options.
options.AdvancedOptions.UseDerivedRangeAnalysis = 1
options =
fxpOptimizationOptions with properties:
MaxIterations: 50
MaxTime: 600
Patience: 15
Verbosity: High
AllowableWordLengths: [8 16 32]
ObjectiveFunction: BitWidthSum
UseParallel: 0
Advanced Options
AdvancedOptions: [1×1 DataTypeOptimization.AdvancedFxpOptimizationOptions]
You can import an fxpOptimizationOptions object into the Fixed-Point Tool to perform data type optimization in the app. By importing an fxpOptimizationOptions object rather than specifying settings manually in the app, you can easily save and restore your settings.
Open the model.
model = 'ex_controllerHarness';
open_system(model);To specify options for the optimization, such as the allowable word length and number of iterations, use the fxpOptimizationOptions object.
options = fxpOptimizationOptions('AllowableWordLengths',[2:32],... 'MaxIterations',3e2,... 'Patience',50);
Open the Fixed-Point Tool with the Controller subsystem selected.
fxptdlg('ex_controllerHarness/Controller')In the Fixed-Point Tool, select New > Optimized Fixed-Point Conversion to start the data type optimization workflow.
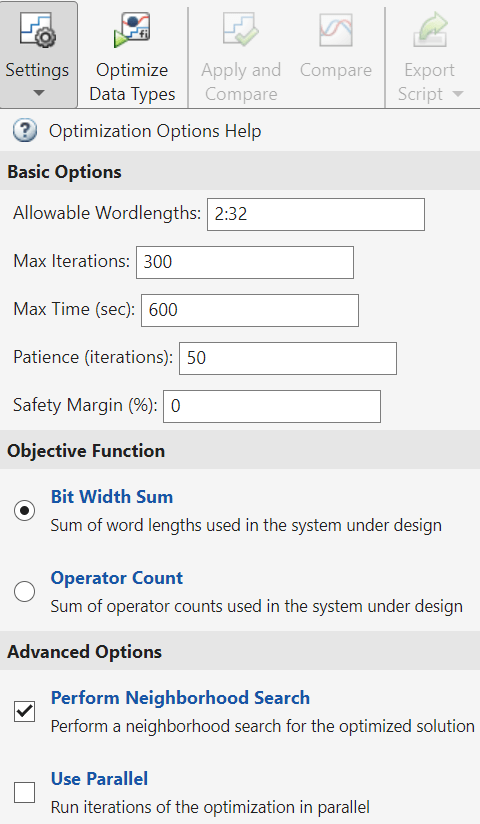
In the Setup pane, under Advanced Options, select the optimization options object to import from the dropdown menu. Click Import.

Expand the Optimization Options menu in the toolstrip to confirm that the optimization options were applied.
Version History
Introduced in R2018aUsing the fxpOptimizationOptions object, you can now specify to
automatically replace unsupported constructs with a lookup table
approximation.
options.AdvancedOptions.HandleUnsupported = "ReplaceLUT"You can now restrict instrumentation to a subsystem by using the
InstrumentationContext property of the
fxpOptimizationOptions object to specify the subsystem to use for
instrumentation and range collection.
You can now choose to display a warning message when fxpopt
encounters blocks that are not supported for data type conversion, in addition to the
existing options to isolate or error. To warn for unsupported constructs, set the
HandleUnsupported property of the
fxpOptimizationOptions object to 'Warn'.
You can now override data types in a model with scaled doubles.
See Also
Apps
Classes
Functions
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Seleccione un país/idioma
Seleccione un país/idioma para obtener contenido traducido, si está disponible, y ver eventos y ofertas de productos y servicios locales. Según su ubicación geográfica, recomendamos que seleccione: .
También puede seleccionar uno de estos países/idiomas:
Cómo obtener el mejor rendimiento
Seleccione China (en idioma chino o inglés) para obtener el mejor rendimiento. Los sitios web de otros países no están optimizados para ser accedidos desde su ubicación geográfica.
América
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europa
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)