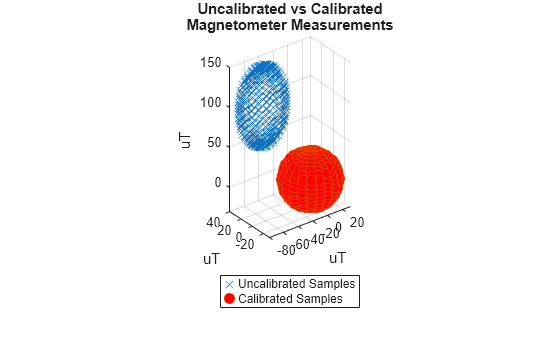
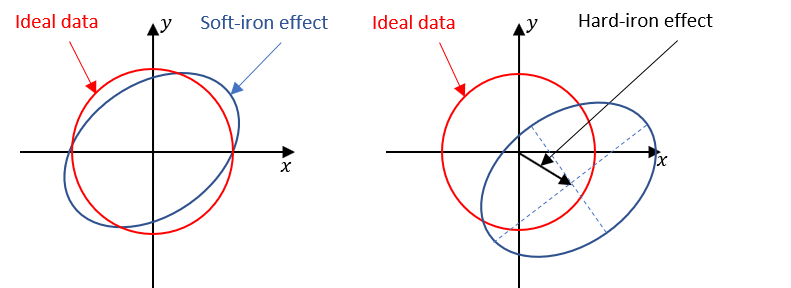
magcal
Coeficientes de calibración del magnetómetro
Descripción
Ejemplos
Argumentos de entrada
Argumentos de salida
Más acerca de
Referencias
[1] Ozyagcilar, T. "Calibrating an eCompass in the Presence of Hard and Soft-iron Interference." Freescale Semiconductor Ltd. 1992, pp. 1-17.